| Date | November 2010 | Marks available | 5 | Reference code | 10N.3.HL.TZ0.H1 |
| Level | Higher level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | Time zone 0 |
| Command term | Discuss | Question number | H1 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
This question is about a Galilean transformation and time dilation.
Ben is in a spaceship that is travelling in a straight-line with constant speed v as measured by Jill who is in a space station.
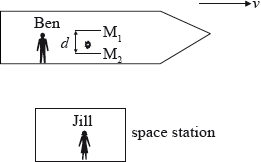
Ben switches on a light pulse that bounces vertically (as observed by Ben) between two horizontal mirrors \({{\text{M}}_{\text{1}}}\) and \({{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}\) separated by a distance \(d\). At the instant that the mirrors are opposite Jill, the pulse is just leaving the mirror \({{\text{M}}_{\text{2}}}\). The speed of light in air is \(c\).
The questions (e) and (f ) introduce the concepts of time dilation and length contraction. Discuss how muon decay in the atmosphere provides experimental evidence for these concepts.
Markscheme
Look for these main points however expressed.
muons produced in the upper atmosphere have speeds close to \(c\);
many such muons are observed reaching the surface of Earth;
the half-life as measured in a muon’s frame of reference does not give time for many to reach Earth / means many will have decayed in travelling to Earth;
but the contracted length of the journey/length as measured in a muon’s reference frame means there is sufficient time;
and the dilated time/time measured by Earth observer is also sufficient for muons to reach the surface;
Examiners report
Parts (f) and (g) were HL only with the length contraction usually done correctly in (f). There were, however, many confused ideas in the discussion of muon decay and it‟s bearing on time dilation and length contraction. Rarely were there any attempts to identify the two reference frames involved, that of the muons and that of the Earth. Many candidates as in previous years still have the idea that there is an absolute reference frame and so talk about time going more slowly for moving objects.

