| Date | May 2013 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 13M.2.sl.TZ1.3 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Compare | Question number | 3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Both sodium and sodium chloride can conduct electricity.
Compare how electric current passes through sodium and sodium chloride by completing the table below.
Sodium can be obtained by electrolysis from molten sodium chloride. Describe, using a diagram, the essential components of this electrolytic cell.
Markscheme
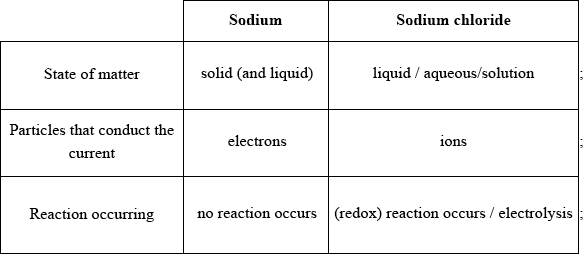
Award [1] for each feature that is correct for both sodium and sodium chloride.
Accept equation or half-equations for the reaction of sodium chloride in “reaction occurring”.
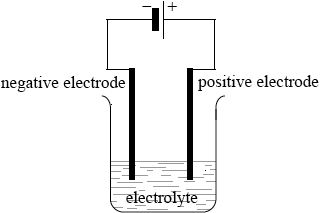
clear diagram containing all elements (power supply, connecting wires, electrodes, container and electrolyte);
labelled positive electrode/anode and negative electrode/cathode;
Accept positive and negative by correct symbols near power supply.
Accept power supply if shown as conventional long/short lines (as in diagram above) or clearly labelled DC power supply.
labelled electrolyte/NaCl(l);
State of NaCl not needed.
Examiners report
Very poorly answered. The state of matter received most marks, conducting particles seldom correct and reaction occurring generally misunderstood by candidates.
Diagrams were very poorly drawn, many without power supplies and the wires within the electrolyte. The electrodes were often mis-signed as Na and/or Cl. Many candidates seem to confuse voltaic cells with electrolytic cells.

