| Date | May 2014 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 14M.3.hl.TZ2.12 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Outline and State | Question number | 12 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Ethene can be polymerized to form poly(ethene) and, depending on the conditions used, either high-density poly(ethene) (HDPE) or low-density poly(ethene) (LDPE) is formed.
(i) Other than density, state two differences in the physical properties of HDPE and LDPE.
(ii) Outline how the differences in (a)(i) relate to differences in their chemical structure.
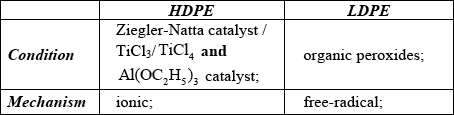
State the conditions required to produce HDPE and LDPE and the name of each type of mechanism involved.
Markscheme
(i) Award [1] for any two.
HDPE has higher mp;
HDPE is more rigid / less flexible;
HDPE is stronger;
Accept opposite statements for LDPE.
(ii) HDPE has straight chain and LDPE has branched chain / LDPE has more branched chains;
Examiners report
HDPE and LDPE in Q12 needed two different physical properties and it was important to compare the structures. The conditions of their formation were less well answered than the mechanisms.
HDPE and LDPE in Q12 needed two different physical properties and it was important to compare the structures. The conditions of their formation were less well answered than the mechanisms.

