| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.3.hl.TZ2.18 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 18 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
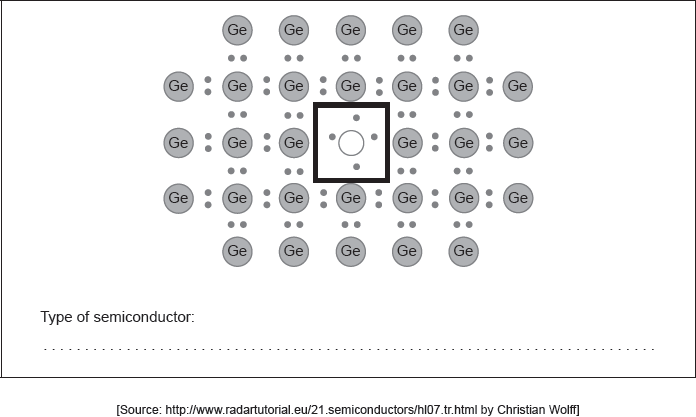
The conductivity of a germanium semiconductor can be increased by doping.
A dye-sensitized solar cell uses a ruthenium(II)–polypyridine complex as the dye. Two ruthenium(II) complexes, A and B, absorb light of wavelengths 665 nm and 675 nm respectively.
Draw the Lewis (electron dot) structure for an appropriate doping element in the box in the centre identifying the type of semiconductor formed.
State the feature of the molecules responsible for the absorption of light.
Outline why complex B absorbs light of longer wavelength than complex A.
Markscheme
ALTERNATIVE 1
B/Ga in circle AND Type of semiconductor: p-type
showing 3 electron pairs AND one lone electron «and hole»
ALTERNATIVE 2
P/As in circle AND Type of semiconductor: n-type
showing 4 electron pairs AND one non-bonded electron
Accept any group 13 element labelled as p-type.
Accept showing 7 electrons.
Accept any group 15 element labelled as n-type.
Accept showing 9 electrons.
Accept dots or crosses for electrons.
[2 marks]
conjugated C=C/carbon–carbon double bonds
OR
«multiple» alternating C=C/carbon–carbon double bonds
OR
«extensive electron» conjugation/delocalization
OR
«many» fused/conjugated aromatic/benzene rings
[1 mark]
complex B has greater conjugation/delocalization
[1 mark]

