| Date | May 2012 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 12M.3.hl.TZ2.A4 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | A4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Transition metal complexes are coloured because electronic transitions occur within split d orbital energy levels. Identify two different factors that affect the colour of complexes of a specific transition metal.
Phenolphthalein indicator is colourless in solutions with a pH less than 8.2 but pink in solutions with a pH greater than 10.0. The molecule dissociates according to the equation:
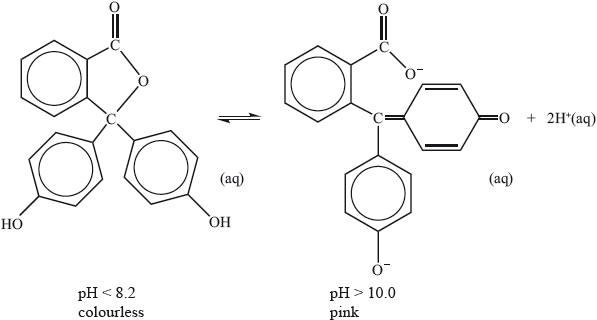
Explain, in terms of the structures, why the indicator is colourless at \({\text{pH}} < 8.2\) and is pink at \({\text{pH}} > 10.0\).
Markscheme
oxidation state of transition element/number of d electrons/charge on ion;
type/identity/charge density of ligands;
stereochemistry/shape of complex/number of ligands;
molecule colourless because energy absorbed in UV region/not absorbed in visible region;
anion pink because of greater conjugation/more alternating single and double (C=C) bonds;
anion/coloured form/more conjugated form absorbs in visible region/lower energy radiation/green light;
complementary colour seen;
Examiners report
Many scored both marks in (a), although some blanks were seen.
Part (b) was generally well answered, with most showing a good understanding of the material being tested, although a few referred to d-d electron transitions.

