| Date | May 2010 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 10M.3.hl.TZ2.A5 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | A5 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
\(\beta \)-carotene is involved in the formation of vitamin A. Its sources include carrots, broccoli and dark, leafy vegetables. Its structure is shown below.
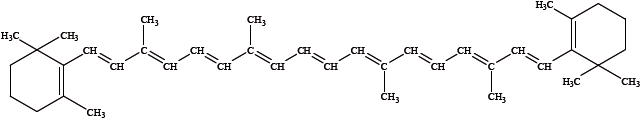
Explain whether\(\beta \)-carotene absorbs ultraviolet or visible radiation.
Markscheme
extensive conjugation of (C=C) double bonds / alternate single and double (carbon–carbon) bonds / involving delocalization of \(\pi \) electrons;
less energy is required (to excite the electrons);
absorption occurs in the visible region;
Examiners report
Candidates recognised that \(\beta \)-carotene consisted of conjugated C=C double bonds but often answered, that because of this it absorbed ultraviolet radiation. Few candidates could explain that less energy was required to excite the electrons due to the conjugation.

