| Date | November 2011 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 11N.2.hl.TZ0.9 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 9 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Consider the following reactions.
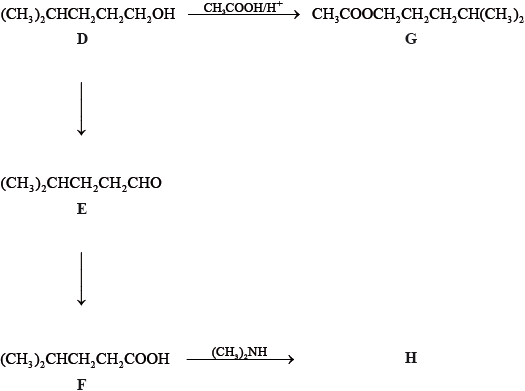
State the IUPAC names of each of the compounds, D, E, F and G.
D:
E:
F:
G:
State the reagents and reaction conditions used to convert D to E and D to F directly.
Discuss the volatility of E compared to F.
Markscheme
D: 4-methylpentan-1-ol;
Allow 4-methyl-1-pentanol.
E: 4-methylpentanal;
F: 4-methylpentanoic acid;
G: 4-methylpentyl ethanoate;
Allow 4-methylpentyl acetate.
Award [2] for all four correct, [1 max] for two or three correct.
Award [1 max] if all suffices correct but prefix (4-methyl or pent) not correct.
For both reactions reagents:
named suitable acidified oxidizing agent;
Suitable oxidizing agents are potassium dichromate(VI)/K2Cr2O7 / sodium dichromate(VI)/Na2Cr2O7 / dichromate/Cr2O72– / potassium manganate(VII)/potassium permanganate/KMnO4 / permanganate/manganate(VII)/MnO4–.
Accept H+/H2SO4 instead of sulfuric acid and acidified.
Allow potassium dichromate or sodium dichromate (i.e. without (VI)) or potassium manganate (i.e. without (VII).
Conditions:
distillation for D to E and reflux for D to F;
Award [1 max] if correct reagents and conditions identified for one process only.
Volatility:
E more volatile than F;
hydrogen bonding in carboxylic acid/F;
Accept converse argument.
Examiners report
Many candidates only scored one mark.
Distillation often was not mentioned.
(iv) was very well answered.

