 Newton's third law (N3) tells us about the interaction between two bodies. A casual statement of this law is "all forces have an equal and opposite reaction". However, this throws up a couple of confusing ideas:
Newton's third law (N3) tells us about the interaction between two bodies. A casual statement of this law is "all forces have an equal and opposite reaction". However, this throws up a couple of confusing ideas:
- Why do objects ever move?
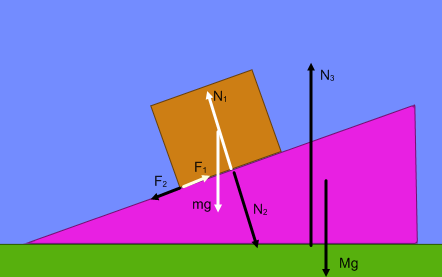
- Is a normal force a reaction to an object's weight?
Key Concepts
If body A exerts a force on body B, body B exerts an equal and opposite force on body A.
It is important to note that Newton's third law only applies in the following circumstances:
- The forces act on different bodies.
- The forces are the same type.
- The forces are the same size.
- The forces act in opposite directions.
Therefore, body A is perfectly capable of accelerating, as the reaction force does not act on A. And the Newton's Third Law pair to an object's weight is the gravitational force on the Earth. We will consider these misconceptions in more detail below.
We know from conservation of momentum that an increase in mass must lead to a reduction in speed (assuming no external forces act). If a trucks collects rocks, the rocks gain momentum but truck loses it.
In terms of forces, this occurs because the truck exerts a forward force on the rocks, accelerating them forward. The rocks exert a backwards force on the truck due to N3, slowing it down.
How much of Newton's third law have you understood?




 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn