 On this page we will consider the gradient of and area under velocity-time graphs and the equations that can be derived from these.
On this page we will consider the gradient of and area under velocity-time graphs and the equations that can be derived from these.
Key Concepts
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity:
\(a={v-u \over t}\)
The SI derived unit of acceleration is m s-2.
All of the equations of motion require constant acceleration.
If the acceleration is constant, average velocity equals the average of the initial and final values. This leads to a suvat equation:
\(s ={(u + v) \over 2}t\)
Collectively these equations are referred to as suvat because of the quantities involved:
- s = displacement /m
- u = initial velocity /m s-1
- v = final velocity /m s-1
- a = acceleration /m s-2
- t = time /s
How much of Linear acceleration have you understood?


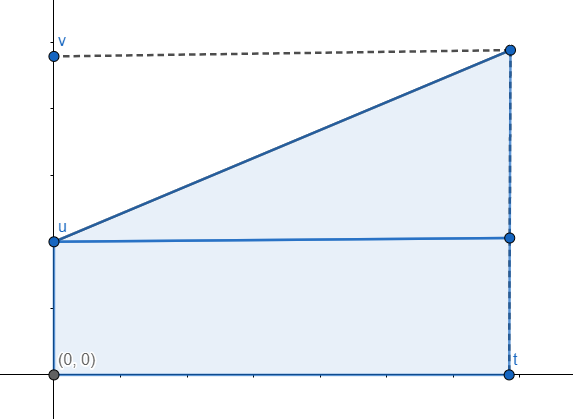 The gradient of a velocity-time graph = Δv/Δt, this is the acceleration:
The gradient of a velocity-time graph = Δv/Δt, this is the acceleration:




 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn