- Summary list for topic 4.3 Carbon cycle
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about the carbon cycle.
- Model answer
- Model answer
- 4.3 Carbon cycle quiz 1/1
 The processes of the carbon cycle include photosynthesis and respiration which are well known, but this topic gets tricky in other connected aspects of the global carbon cycle. These include storage of carbon containing molecules in peat, fossil fuels, coral, and the oceans. An understanding of diffusion and dissolving are also required. This revision page covers these details.
The processes of the carbon cycle include photosynthesis and respiration which are well known, but this topic gets tricky in other connected aspects of the global carbon cycle. These include storage of carbon containing molecules in peat, fossil fuels, coral, and the oceans. An understanding of diffusion and dissolving are also required. This revision page covers these details.These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for topic 4.3 Carbon cycle
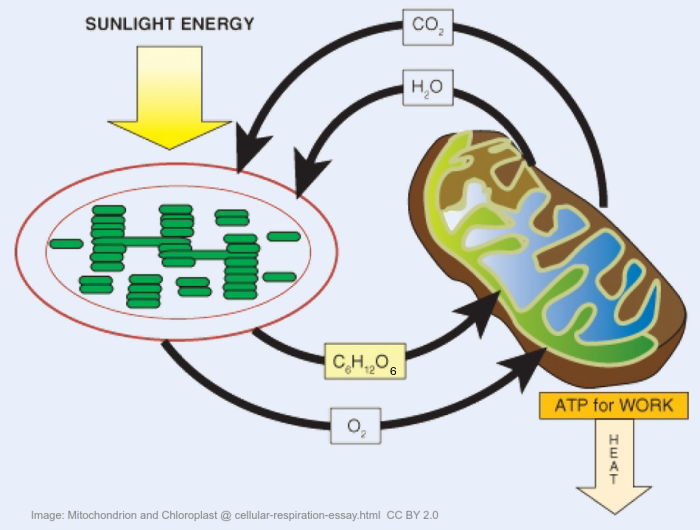
- Carbon dioxide is converted (by photosynthesis) into carbohydrates and other carbon compounds in autotrophs.
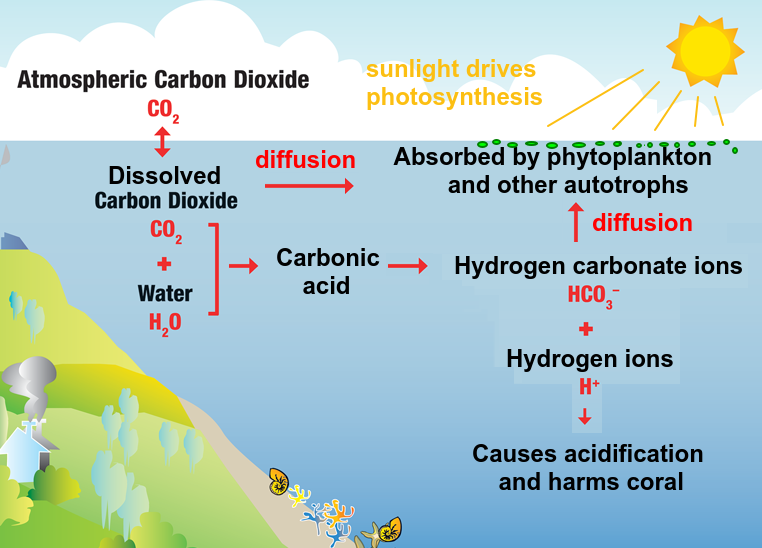
- Carbon is present as dissolved carbon dioxide and hydrogen carbonate ions (HCO3-) in aquatic ecosystems.
- Carbon dioxide moves from the atmosphere or water into autotrophs by diffusion.
- Carbon dioxide is produced by respiration and diffuses out of organisms into water or the atmosphere.
- Methane (CH4) is produced from decaying organic matter in anaerobic conditions by bacteria.
- Methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water in the atmosphere.
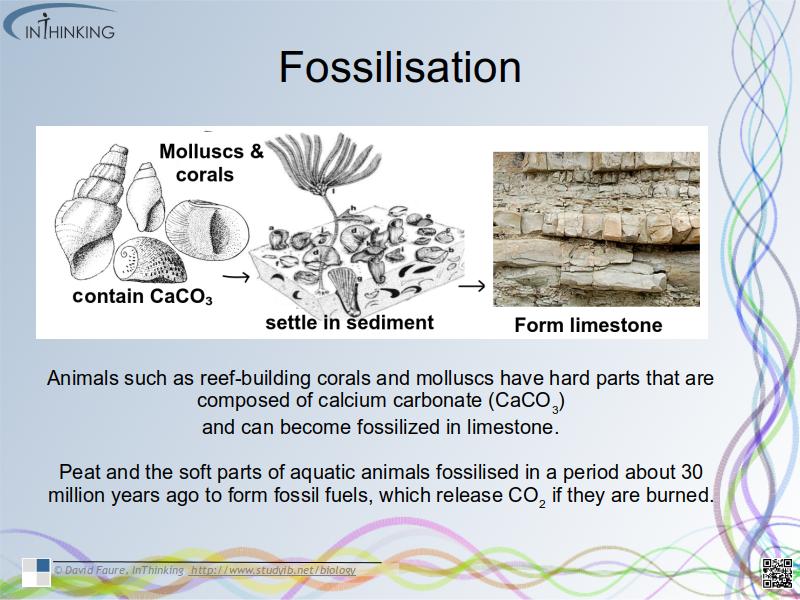
- Peat forms when organic matter is not fully decomposed in waterlogged soils.Organic matter was converted into coal, oil and gas that accumulate in porous rocks.
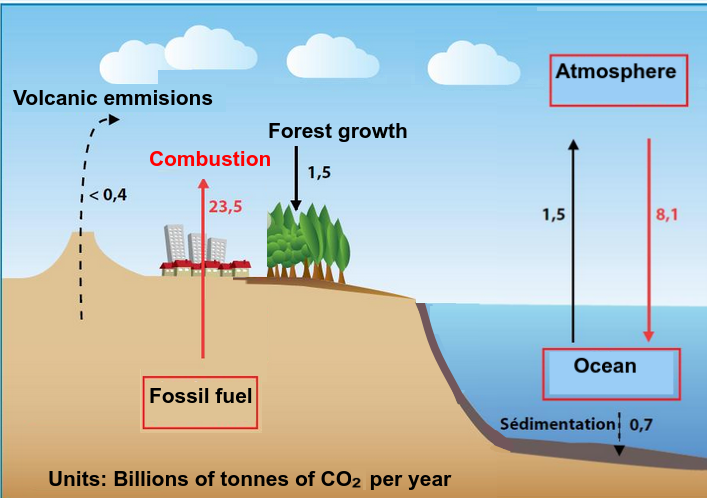
- Carbon dioxide is produced by the combustion of biomass and fossil fuels.
- Animals such as reef-building corals and mollusca have hard parts that are composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)and can become fossilized in limestone.
- Students need an awareness that carbon fluxes are estimates.
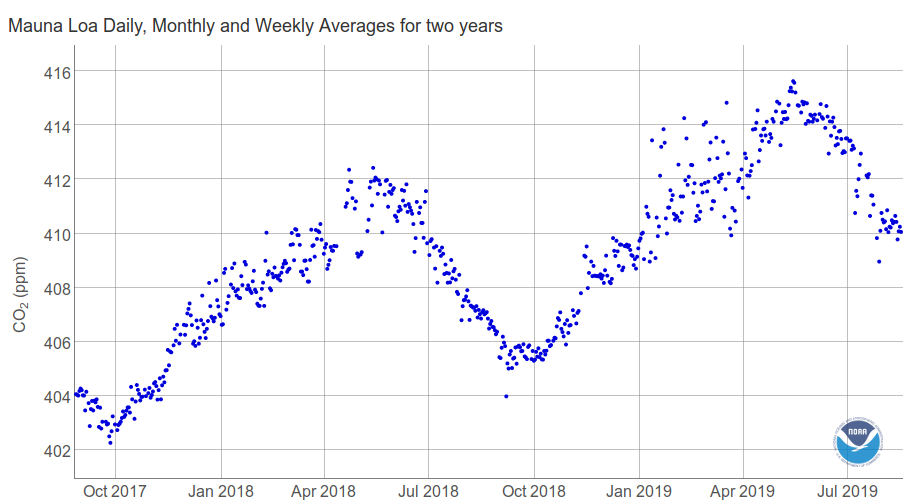
- Experience of the analysis of data from air monitoring stations.
- The skill to draw a diagram of the carbon cycle.
Mindmaps
These diagram summaries cover the main sections of topic 4.3 Carbon cycle.
Study them and draw your own list or concept map, from memory if you can.
Exam style question about the carbon cycle.
Explaining the different processes is an important skill from this topic.
Answer the question below, on a piece of paper, then check your answer against the model answer below.
The diagram below shows part of the carbon cycle.
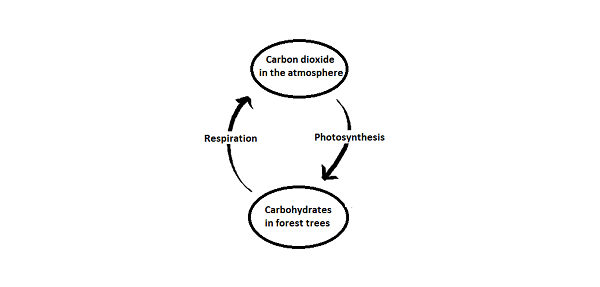
Add carbon reservoirs to the diagram and draw arrows connecting them showing the processes which control carbon fluxes. [4]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
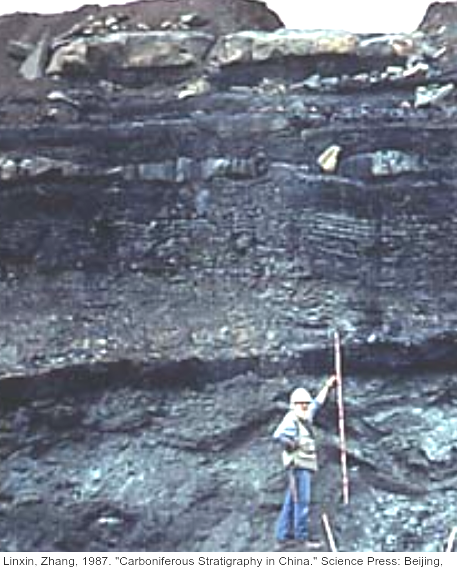
The image shows peat turf that is being dug from a peat bog.
Drag and drop the correct word or phrase into the gap to describe peat formation.

detritivores decomposers acidic oxygen fossilised partially organic carbon dioxide completely oil alkaline anaerobic agriculture
Peat is decomposed matter. It forms in waterlogged soils where insufficient is present for rapid recycling. It becomes due to the accumulation of organic acids from partial breakdown of dead plant material by respiration of . It is used as fuel and in as fertiliser. In past epochs, it was under pressure to to form coal, or gas which became trapped in porous rocks.
Waterlogging of dead plant material prevents full decomposition of organic matter due to lack of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration forms acids, giving a low pH further slowing decomposition.
Everyone needs a bit of fun while they revise. Try this Carbon cycle card matching game.
Can you reach the leader board?
How much of Carbon Cycle 4.3 have you understood?

























 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn