- Summary list for topic 3.1 Chromosomes
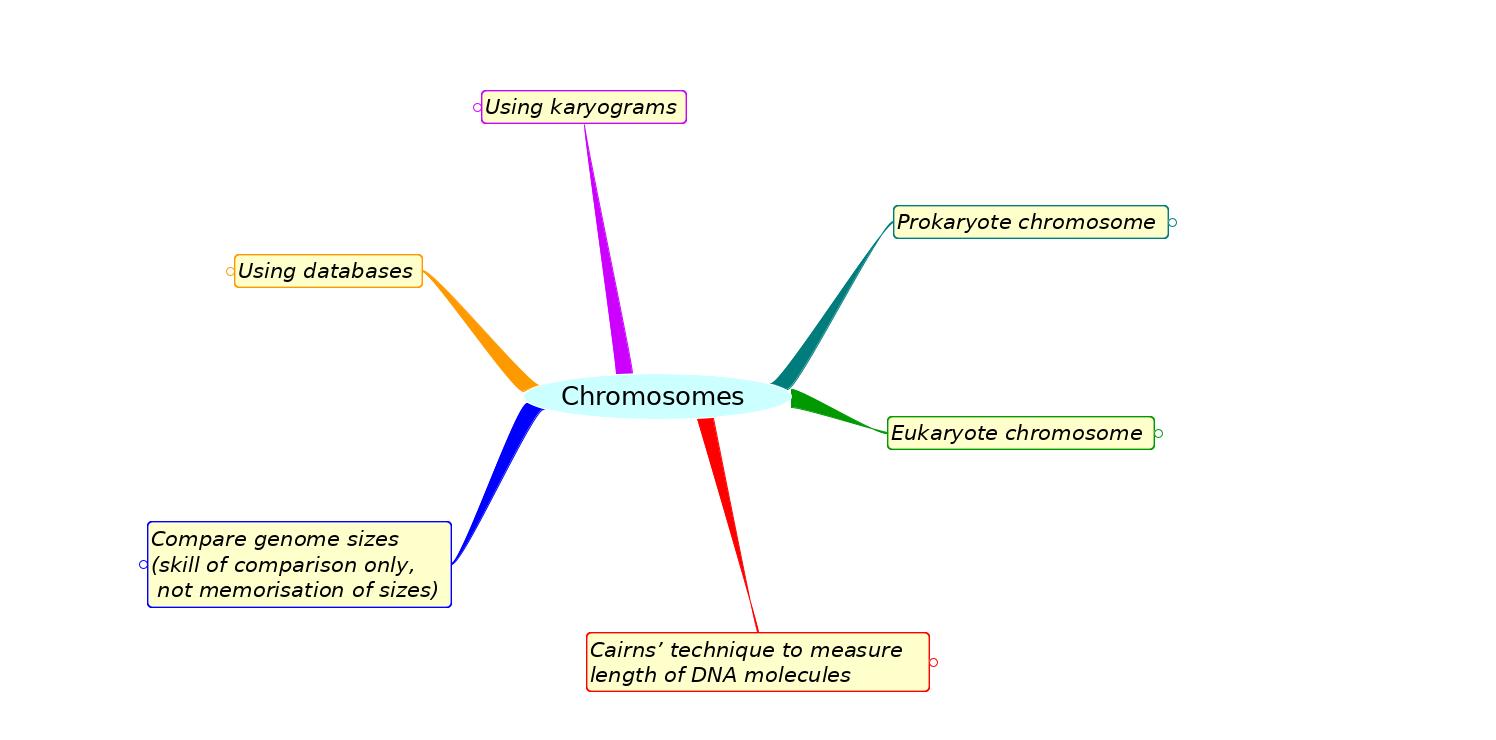
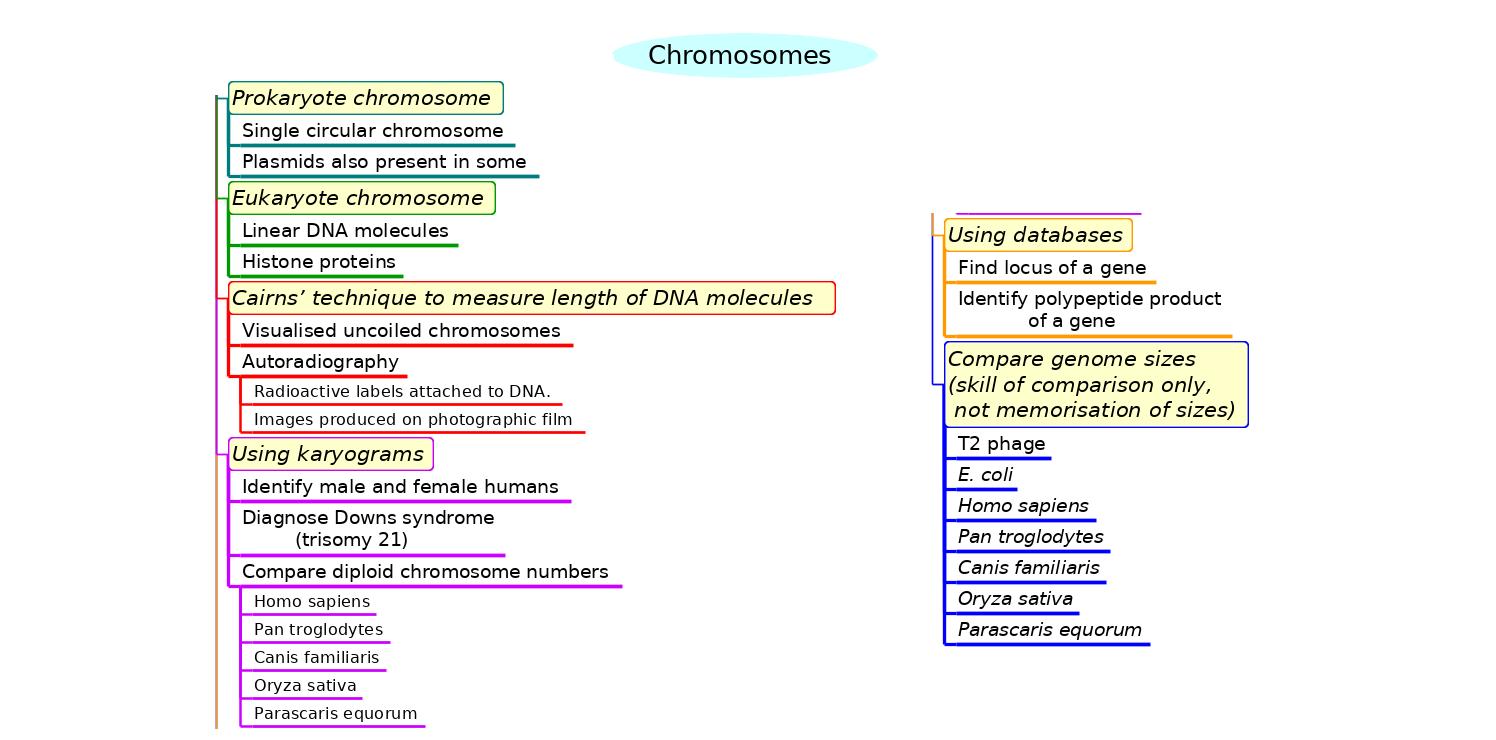
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about chromosomes
- Model answer
- Model answer
- 3.2 Chromosomes 1/1
These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - good revision for all students.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for topic 3.1 Chromosomes
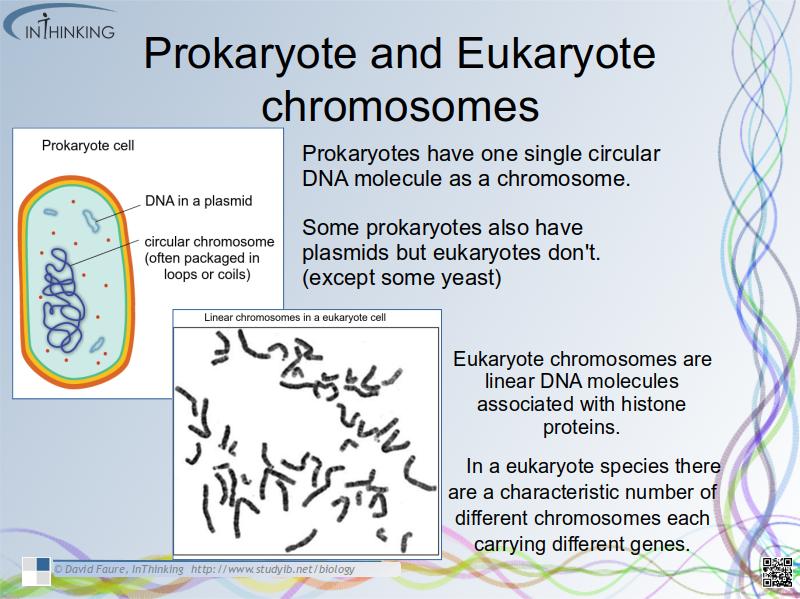
- Prokaryotes have one single circular DNA molecules as a chromosome.
- Some prokaryotes also have plasmids but eukaryotes don't.
- Eukaryote chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins.
- In a eukaryote species there are a characteristic number of different chromosomes each carrying different genes.
- Pairs of chromosomes with the same sequence of genes (not necessarily the same alleles) are "Homologous chromosomes".
- Diploid nuclei have pairs of homologous chromosomes.
- Haploid nuclei have one chromosome of each pair.
- Sister chromatids are the two DNA molecules formed by DNA replication before cell division.
- two separate chromosomes are formed at the splitting of the centromere at the start of anaphase.
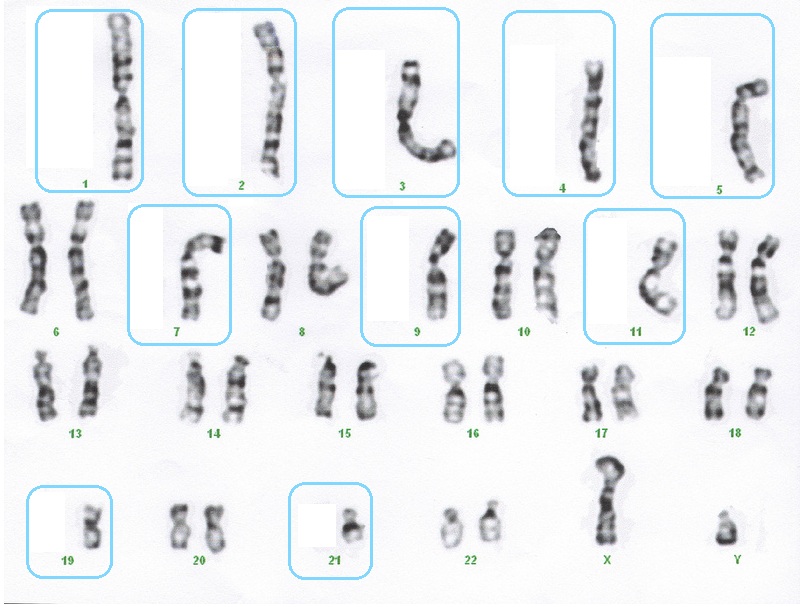
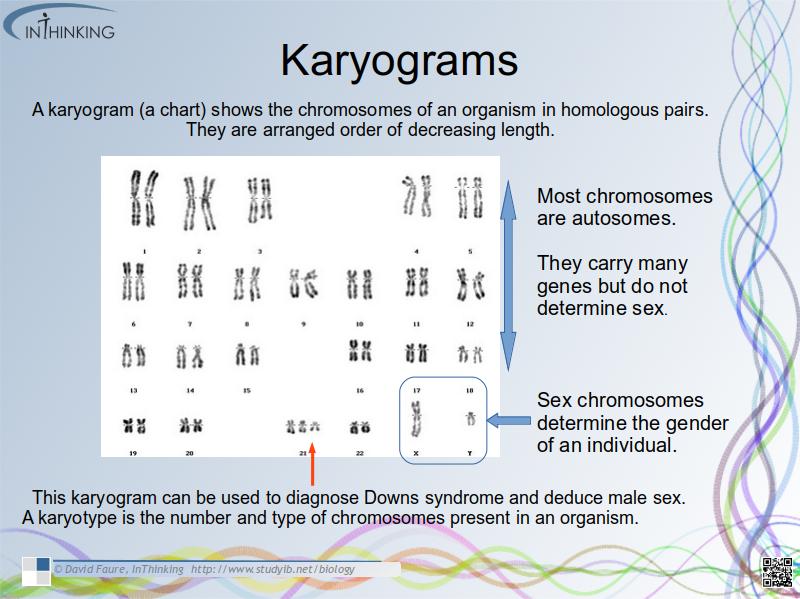
- A karyogram shows the chromosomes of an organism in homologous pairs of decreasing length. (Note: karyotype is the number and type of chromosomes present in the nucleus, while a karyogram is a diagram of these).
- Sex chromosomes determine the gender of an individual and autosomes are chromosomes that do not determine sex.
Applications (can you ....)
- Understand Cairns’ technique for measuring the length of DNA molecules by autoradiography.
- Compare genome size in T2 phage, Escherichia coli, Drosophila melanogaster, Homo sapiens and Paris japonica. (selected for points of interest.Genome size comparative activity.
- Use karyograms to compare diploid chromosome numbers of Homo sapiens, Pan troglodytes, Canis familiaris, Oryza sativa, Parascaris equorum.
- Use karyograms to deduce sex and diagnose Down syndrome in humans.
- Use of databases to identify the locus of a human gene and its polypeptide product.
Mindmaps
These diagram summaries cover the main details of topic 3.2 Chromosomes
Study them and draw your own list or concept map, from memory if you can.
Exam style question about chromosomes
The skill of deducing sex and diagnosing Down syndrome using karyograms is important in this topic.
Answer the question below on a piece of paper, then check your answer with the model answer.
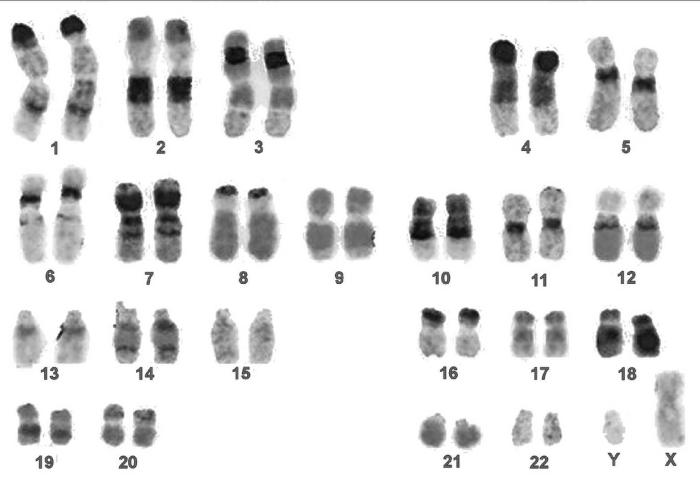
The image shows karyograms from three different people.
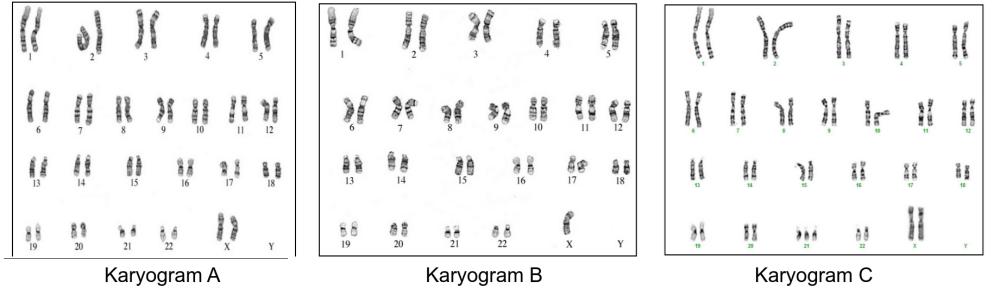
Analyse these karyotypes, giving a statement about the genetic condition and an explanation [3]
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
A quiz containing multiple choice questions covering the understanding and skills from this topic.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
There are differences in the nature of the chromosomes in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Complete the table of comparison by dragging and dropping the correct word or phrase into the gap in the table.
cell histone Linear. branched chromosome 1 only proteins Single absent one set Circular. 1 pair
Chromosome | Prokaryote | Eukaryote |
Number of chromosomes |
| 2 or more
|
Gene content of chromosomes | chromosome that has of genes. | Each has a unique set of genes. |
Shape of chromosome |
|
|
Structure of the chromosomes | No association with (naked). | Associated with proteins. |
Plasmids | May have plasmids containing a few genes. | Plasmids . |
Examiner hint: A table is a good method to draw comparisons.
How much of Chromosomes 3.2 have you understood?



















 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn