- Summary list for 8.1 Metabolism
- Mindmaps
- Exam style question about enzymes
- Model answer
- Exam style question about the role of specific enzymes.
- Model answer
- Model answer
- Multiple choice questions
- 8.1 Enzymes and metabolism 1/1
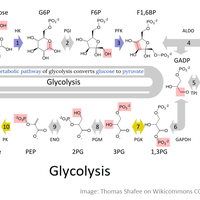 This topic covers the way enzyme pathways form a cell's metabolism as well as specific examples of these pathways. The action of enzymes and their substrates is required as well as the way in which competitive and non-competitive inhibitors change the rate of reaction. The skill of calculating a rate of reaction from a graph of data is also part of this topic.
This topic covers the way enzyme pathways form a cell's metabolism as well as specific examples of these pathways. The action of enzymes and their substrates is required as well as the way in which competitive and non-competitive inhibitors change the rate of reaction. The skill of calculating a rate of reaction from a graph of data is also part of this topic.These slides summarise the essential understanding and skills in this topic.
They contain short explanations in text and images - great revision.
Read the slides and look up any words or details you find difficult to understand.
Summary list for 8.1 Metabolism
Metabolic pathways
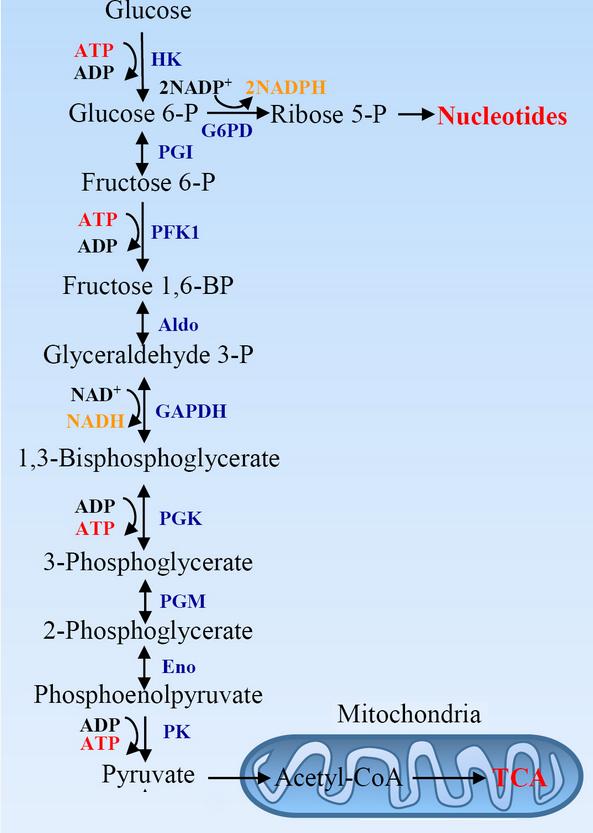
- A chain or a cycle of enzyme-catalysed reactions makes a metabolic pathway.
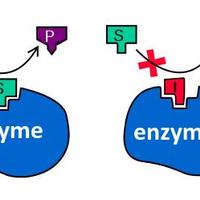
- Enzymes catalyse chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy.
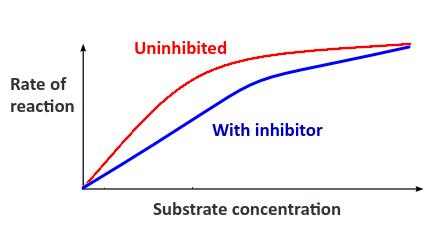
Competitive inhibitors
- Competitive inhibitors for example in medicine - ethanol and Fomepizole used as competitive inhibitors for antifreeze poisoning.
Non-competitive inhibitors
- Non-competitive inhibitors. E.g. Drugs for treatment of malaria.
- End-product inhibition can control metabolic pathways - e.g. In the pathway that converts threonine to isoleucine.
Skills
- The use of databases to identify potential new anti-malarial drugs. In the ER role play: students will have seen this
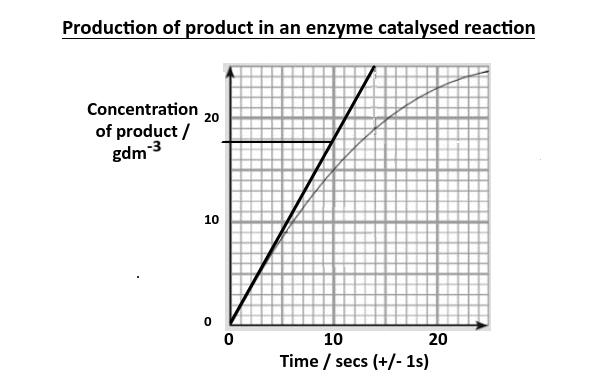
- In the Enzyme inhibition experiment students will calculate and plot rates of reaction from raw experimental results.
- They will also distinguish different types of inhibition from graphs at specified substrate concentration.
Mindmaps
These diagram summaries cover the main sections of topic 8.1 Metabolism
Study them and draw your own list or concept map from memory.
Exam style question about enzymes
Answer the question below, which addresses the role of enzymes.
Explain how enzymes increase rates of reaction in metabolic pathways. (4 marks)
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
....................................................................................... ............................................................................
Click the + icon to see a model answer.
Multiple choice questions
This is a self marking quiz containing questions covering the topic outlined above.
Try the questions to check your understanding.
START QUIZ!
Drag and drop activities
Test your ability to construct biological explanations using the drag and drop questions below.
Competitive inhibition of enzymes and antibiotics
You need to know specific examples of enzyme inhibition.
Drag and drop the correct term into the gap to describe the use of antibiotics as enzyme inhibitors.
temporarily cell wall active site competitive binary fission substrate slowing "look-alike" metabolic pathways
Nonpermanent competitive enzyme inhibitors bind to the of an enzyme in competition with the . As they are noncompetitive, they bind to the active site, the rate of reaction but do not damage the enzyme. They are generally molecules with a very similar molecular shape to the substrate, molecules
Beta lactams are antibiotics which act as inhibitors of the enzymes in bacteria which synthesise peptidoglycans, a polymer found in bacterial cell walls. They bind to the active site of the enzyme, preventing it from completing the structure when the bacterium divides by .
They do not harm humans (bar possible side effects) as the enzyme is not found in human as human cells do not have a cell wall.
Explanation. Many antibiotics are inhibitors of prokaryotic enzymes, not found in animal eukaryotes. They are ineffective against viruses because they use host metabolic pathways.
How much of Metabolism 8.1 HL have you understood?













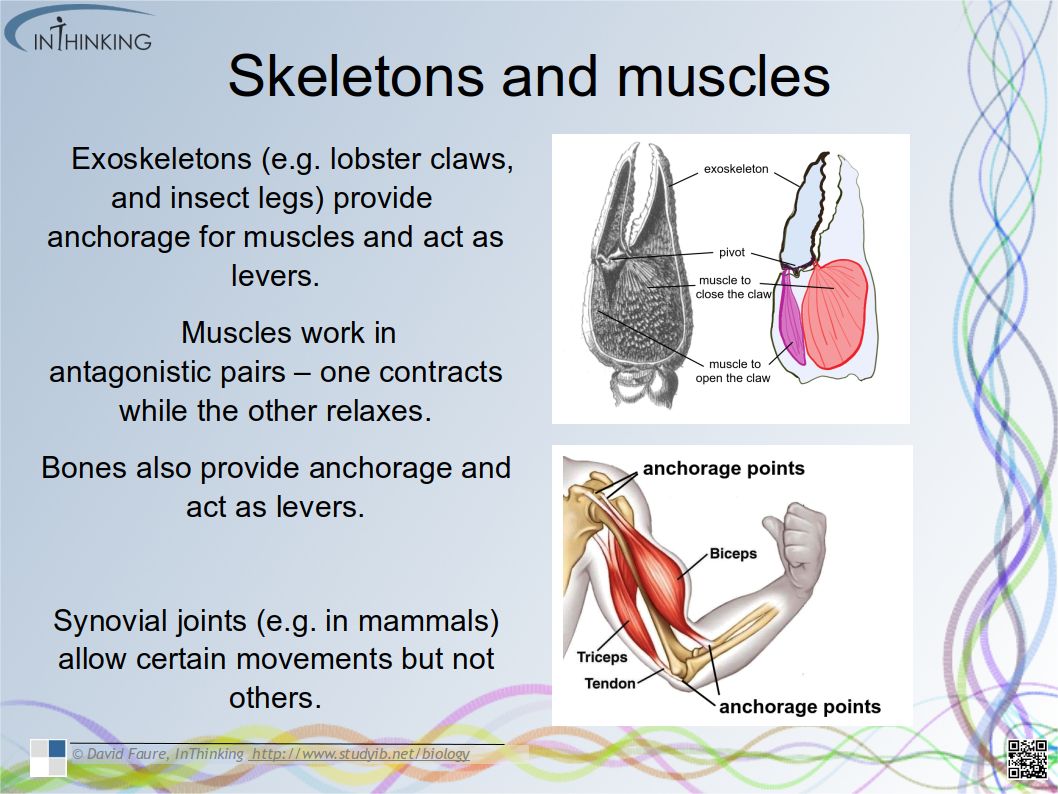
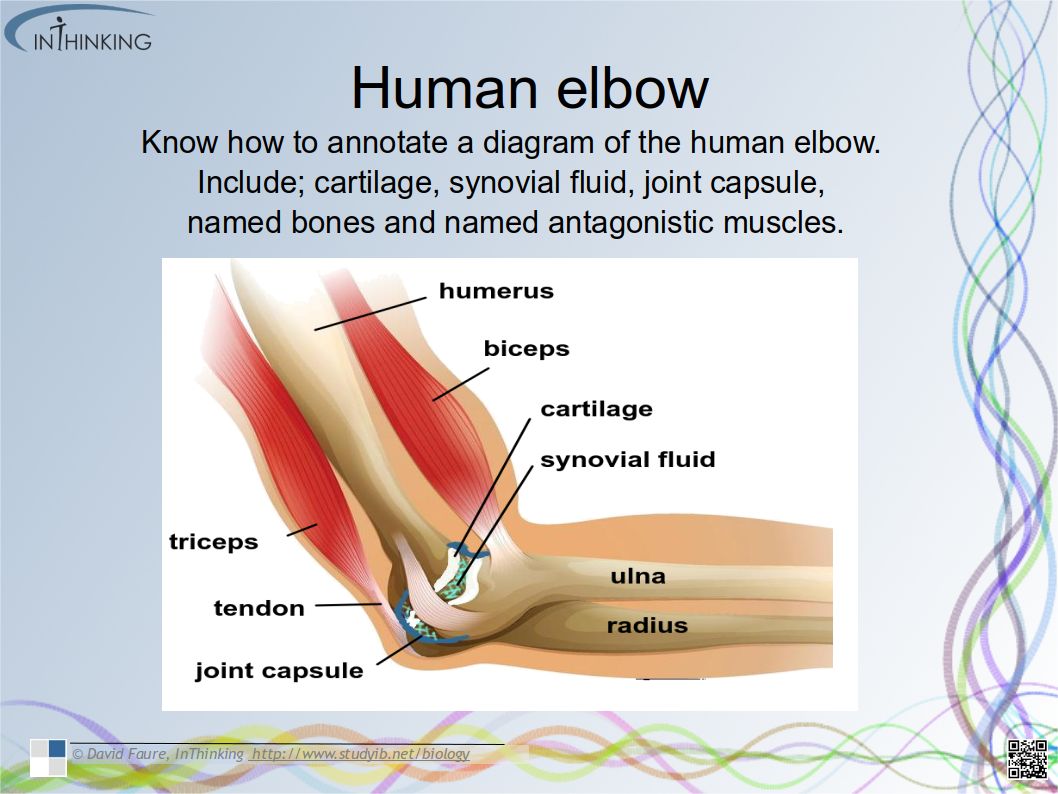
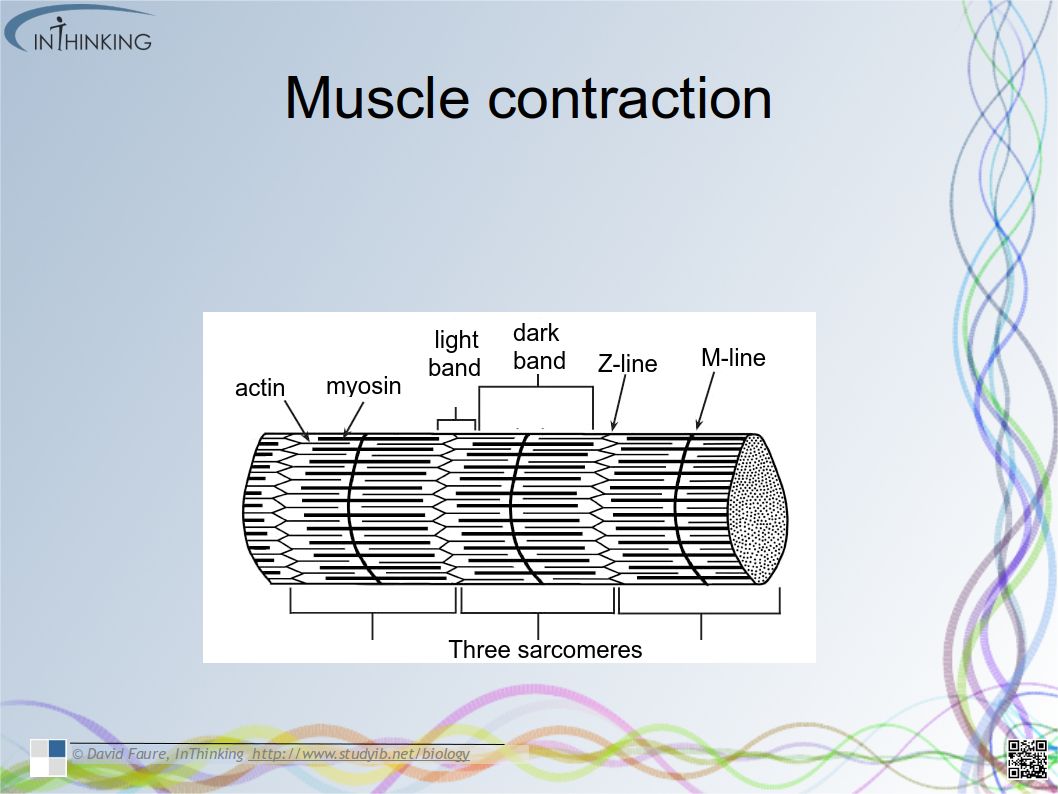









 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn