| Date | November 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18N.3.sl.TZ0.11 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Identify | Question number | 11 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Solar energy, which is freely available, is indispensable to life on earth.
Suggest another advantage and one disadvantage of solar energy.
Light can be absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments.
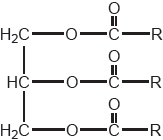
Consider molecules A and B represented below.
Identify, with a reason, the molecule that absorbs visible light.
State a physical property of vegetable oils that makes them very difficult to use as fuel in internal combustion engines.
Describe how vegetable oils can be converted to a more suitable fuel.
Contrast the importance of carbon dioxide and methane as greenhouse gases.
Explain, using an equation, the effect of increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere on the pH of lake water.
Markscheme
Advantage:
renewable «energy source»
OR
does not produce greenhouse gases
OR
can be installed «almost» anywhere
OR
low maintenance costs ✔
Disadvantage:
widely dispersed/not concentrated «form of energy»
OR
geography/weather/seasonal dependent
OR
not available at night
OR
energy storage is difficult/expensive
OR
toxic/hazardous materials used in production
OR
concerns about space/aesthetics/local environment where installed
OR
need to be «constantly» cleaned ✔
Accept “can be used for passive/active heating”, “can be converted to electric energy”.
Accept any specific greenhouse gas name or formula for “greenhouse gases”.
Accept “solar cells require large areas”, “solar cell manufacture produces pollution/greenhouse gases”, “higher cost of solar cells «compared with traditional sources such as fossil fuels or hydroelectric»”.
B AND larger/more extensive «electronic» conjugation
OR
B AND «contains» more alternate single and double bonds ✔
Accept more specific statements, such as “sp3 carbon in A prevents conjugation between aromatic rings”.
high viscosity ✔
Accept “low volatility”, just “viscous/viscosity” OR “does not flow easily”.
convert to esters of monoatomic alcohols
OR
react with short-chain alcohols «in the presence of acid or base» ✔
Accept “convert to shorter «carbon chain» esters” OR “transesterification”.
Accept specific alcohols, such as methanol or ethanol.
carbon dioxide/CO2 more/most abundant «GHG than methane/CH4»
OR
carbon dioxide/CO2 has «much» longer atmospheric life «than methane/CH4» ✔
methane/CH4 «much» better/more effective at absorbing IR radiation «than carbon dioxide/CO2»
OR
methane/CH4 has a greater greenhouse factor «than carbon dioxide/CO2»
OR
methane/CH4 has a greater global warming potential/GWP «than carbon dioxide/CO2» ✔
Accept “carbon dioxide/CO2 contributes more to global warming «than methane/CH4»”.
CO2 (g) + H2O (l) H+ (aq) + HCO3– (aq)
OR
CO2 (g) CO2 (aq) AND CO2 (aq) + H2O (l) H+ (aq) + HCO3– (aq) ✔
«increasing [CO2 (g)]» shifts equilibrium/reaction to right AND pH decreases ✔
Accept “H2CO3 (aq)” for “CO2 (aq) + H2O (l)”.
Equilibrium arrows required for M1.
State symbols required for CO2 (g) CO2 (aq) equation only for M1.
Accept “concentration of H+/[H+] increases AND pH decreases” for M2.