| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 18M.2.hl.TZ1.2 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Describe | Question number | 2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Calcium carbide, CaC2, is an ionic solid.
Describe the nature of ionic bonding.
Describe how the relative atomic mass of a sample of calcium could be determined from its mass spectrum.
When calcium compounds are introduced into a gas flame a red colour is seen; sodium compounds give a yellow flame. Outline the source of the colours and why they are different.
Suggest two reasons why solid calcium has a greater density than solid potassium.
Outline why solid calcium is a good conductor of electricity.
Sketch a graph of the first six ionization energies of calcium.
Calcium carbide reacts with water to form ethyne and calcium hydroxide.
CaC2(s) + H2O(l) → C2H2(g) + Ca(OH)2(aq)
Estimate the pH of the resultant solution.
Describe how sigma (σ) and pi () bonds are formed.
Deduce the number of σ and bonds in a molecule of ethyne.
Markscheme
electrostatic attraction AND oppositely charged ions
[1 mark]
multiply relative intensity by «m/z» value of isotope
OR
find the frequency of each isotope
sum of the values of products/multiplication «from each isotope»
OR
find/calculate the weighted average
Award [1 max] for stating “m/z values of isotopes AND relative abundance/intensity” but not stating these need to be multiplied.
[2 marks]
«promoted» electrons fall back to lower energy level
energy difference between levels is different
Accept “Na and Ca have different nuclear charge” for M2.
[2 marks]
Any two of:
stronger metallic bonding
smaller ionic/atomic radius
two electrons per atom are delocalized
OR
greater ionic charge
greater atomic mass
Do not accept just “heavier” or “more massive” without reference to atomic mass.
[2 marks]
delocalized/mobile electrons «free to move»
[1 mark]
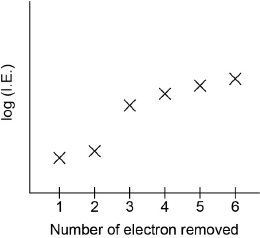
general increase
only one discontinuity between “IE2” and “IE3”
[2 marks]
pH > 7
Accept any specific pH value or range of values above 7 and below 14.
[1 mark]
sigma (σ):
overlap «of atomic orbitals» along the axial/internuclear axis
OR
head-on/end-to-end overlap «of atomic orbitals»
pi ():
overlap «of p-orbitals» above and below the internuclear axis
OR
sideways overlap «of p-orbitals»
Award marks for suitable diagrams.
[2 marks]
sigma (σ): 3
AND
pi (): 2
[1 mark]