| Date | May 2017 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 17M.1.hl.TZ2.10 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 1 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Identify | Question number | 10 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Which does not show resonance?
A. PO43–
B. C6H6
C. C6H12
D. O3
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.6a(iii):
Explain the relative lengths of the three bonds between N and O in nitric acid.
-
17N.1.hl.TZ0.14:
How many sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are present in this molecule?
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.4b.i:
Discuss the bonding in the resonance structures of ozone.
- 18M.1.hl.TZ2.12: Which molecule has an expanded octet? A. CO B. CO2 C. SF2 D. SF4
-
18M.2.hl.TZ2.7c.ii:
Deduce, giving a reason, the more likely structure.
-
22M.1.hl.TZ2.11:
What is the formal charge of the oxygen atom in H3O+?
A. −2
B. −1
C. 0
D. +1
- 22M.1.hl.TZ2.12: What is the molecular geometry of SF4? A. Tetrahedral B. Trigonal bipyramidal C. ...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.13: Which species have resonance structures? I. Ozone, O3II. Carbon dioxide, CO2III. ...
-
18M.1.hl.TZ2.13:
Which overlap of atomic orbitals leads to the formation of only a sigma (σ) bond?
I. s − p
II. p − p
III. s − s
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.2g.ii:
Deduce the number of σ and bonds in a molecule of ethyne.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.4b.ii:
Deduce one resonance structure of ozone and the corresponding formal charges on each oxygen atom.
- 18M.1.hl.TZ1.13: Which can be represented with only one Lewis structure? A. CH2O B. C6H6 C. ...
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.1i:
The C–N bonds in urea are shorter than might be expected for a single C–N bond. Suggest, in terms of electrons, how this could occur.
- 17M.1.hl.TZ2.13: Which statement is correct? A. Sigma bonds are formed only by the combination of s...
-
22M.2.hl.TZ2.7b(i):
Sketch the shape of one sigma () and one pi () bond.
-
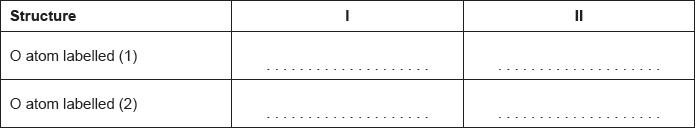
18M.2.hl.TZ2.7c.i:
Carbon dioxide can be represented by at least two resonance structures, I and II.

Calculate the formal charge on each oxygen atom in the two structures.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.3b:
Deduce the Lewis (electron dot) structure and molecular geometry and the bond angles of PCl3.
-
16N.2.hl.TZ0.5b:
(i) Draw diagrams to show how sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are formed between atoms.
(ii) State the number of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in propane and propene.
-
18N.1.hl.TZ0.12:
What is the number of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in the molecule (NC)2C=C(CN)2?
-
18N.2.hl.TZ0.3b.i:
Draw two Lewis (electron dot) structures for BrO3−.
- 18N.2.hl.TZ0.6a.ii: Draw a diagram showing the delocalization of electrons in the conjugate base of butanoic acid.
- 18N.2.hl.TZ0.3b.ii: Determine the preferred Lewis structure based on the formal charge on the bromine atom,...
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.8b:
Suggest why the loss of ozone is an international environmental concern.
- 16N.1.hl.TZ0.15: What is the hybridization of the numbered atoms in ethanoic acid?
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.12: Which combination describes the bonding and structure in benzoic acid, C6H5COOH?
- 19M.1.hl.TZ1.12: Which species has delocalized electrons? A. OH− B. H2CO C. CO2 D. CO32−
-
19M.1.hl.TZ2.12:
How many sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are present in hydrogen cyanide, HCN?
-
22M.2.hl.TZ2.7b(ii):
Identify the number of sigma and pi bonds in HCN.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.2g.i:
Describe how sigma (σ) and pi () bonds are formed.
- 19M.1.hl.TZ2.11: Which species has a square planar molecular geometry? A. SF4 B. XeF4 C. CF4 D. PF4+
-
16N.3.hl.TZ0.22c:
(i) Uranium hexafluoride, UF6, is used in the uranium enrichment process that produces fuel for nuclear reactors.
State the molecular shape of uranium hexafluoride.
(ii) Explain why uranium dioxide, UO2, has a very high melting point whereas uranium hexafluoride vapourises easily into gas.
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.11: Which combination describes the PH4+ ion?
-
16N.1.hl.TZ0.14:
Which species has bond angles of 90°?
A. AlCl4-
B. Cl4-
C. NH4+
D. SiCl4
-
21N.1.hl.TZ0.12:
Which molecules contain two pi () bonds?
I. HCN
II. H2CO3
III. H2C2O4
A. I and II onlyB. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.3d(i):
State what the presence of alternative Lewis structures shows about the nature of the bonding in the molecule.
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.1e(i): Identify the steps which absorb ultraviolet light.
- 19N.2.hl.TZ0.1f: Ozone depletion is catalysed by nitrogen monoxide, NO, which is produced in aircraft and...
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.8a:
Formulate two equations to show how nitrogen(II) oxide, NO, catalyses the destruction of ozone.
-
20N.1.hl.TZ0.11:
Which combination correctly describes the geometry of ?
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.2e:
Outline why both C to O bonds in the conjugate base are the same length and suggest a value for them. Use section 10 of the data booklet.
- 19N.1.hl.TZ0.13: Which atom does not obey the octet rule? A. C in CO2 B. F in BF3 C. O in H2O D. S in SF6
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7c.ii:
Outline, in terms of the bonding present, why the reaction conditions of halogenation are different for alkanes and benzene.
-
17N.2.hl.TZ0.4a:
Draw the Lewis (electron dot) structures of PF3 and PF5 and use the VSEPR theory to deduce the molecular geometry of each species including bond angles.
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.1e(iii):
s produce chlorine radicals. Write two successive propagation steps to show how chlorine radicals catalyse the depletion of ozone.
- 21M.1.hl.TZ1.12: Which contain delocalised electrons? I. C6H5OHII. CH3COO−III. CO32− A. I and II...
-
18M.2.hl.TZ2.7d:
Absorption of UV light in the ozone layer causes the dissociation of oxygen and ozone.
Identify, in terms of bonding, the molecule that requires a longer wavelength to dissociate.
- 21M.1.hl.TZ2.13: What is the electron domain geometry of Si in SiO2? A. bent B. linear C. square...
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.2c:
State the number of sigma () and pi () bonds around the central carbon atom in molecule B.
-
19N.2.hl.TZ0.6f(iii):
When excess ammonia is added to copper(II) chloride solution, the dark blue complex ion, [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+, forms.
State the molecular geometry of this complex ion, and the bond angles within it.
Molecular geometry:
Bond angles:
-
21M.2.hl.TZ2.4d:
Draw diagrams to show how sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds are formed between atoms.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.3a(ii):
Dinitrogen monoxide in the stratosphere is converted to nitrogen monoxide, NO (g).
Write two equations to show how NO (g) catalyses the decomposition of ozone.
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.6a(ii):
Deduce a Lewis (electron dot) structure of the nitric acid molecule, HNO3, that obeys the octet rule, showing any non-zero formal charges on the atoms.
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.5a(iii):
State the number of (sigma) and (pi) bonds in Compound A.
- 21N.2.hl.TZ0.3b(ii): Outline the reason why PCl5 is a non-polar molecule, while PCl4F is polar.
-
21N.2.hl.TZ0.10a(i):
Distinguish between a sigma and pi bond.

