| Date | November 2016 | Marks available | 4 | Reference code | 16N.3.hl.TZ0.21 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Describe and Explain | Question number | 21 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A fuel cell is an energy conversion device that generates electricity from a spontaneous redox reaction.
The Geobacter species of bacteria can be used in microbial fuel cells to oxidise aqueous ethanoate ions,
CH3COO−(aq), to carbon dioxide gas.
State the half-equations for the reactions at both electrodes.
A concentration cell is an example of an electrochemical cell.
(i) State the difference between a concentration cell and a standard voltaic cell.
(ii) The overall redox equation and the standard cell potential for a voltaic cell are:
Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + Cu (s) Eθcell = +1.10 V
Determine the cell potential E at 298 K to three significant figures given the following concentrations in mol dm−3:
[Zn2+] = 1.00 × 10−4 [Cu2+] = 1.00 × 10−1
Use sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet.
(iii) Deduce, giving your reason, whether the reaction in (b) (ii) is more or less spontaneous than in the standard cell.
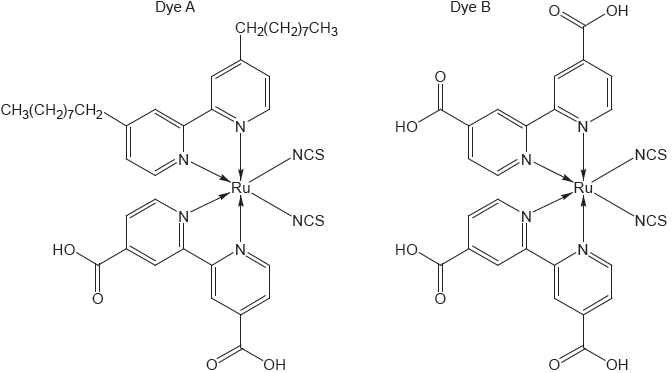
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSC) convert solar energy into electrical energy.
(i) Describe how a DSSC converts sunlight into electrical energy.
(ii) Explain the role of the electrolyte solution containing iodide ions, I−, and triiodide ions, I3−, in the DSSC.
Markscheme
Negative electrode (anode): CH3COO− (aq) + 2H2O (l) → 2CO2 (g) + 7H+ (aq) + 8e−
Positive electrode (cathode): O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e− → 2H2O (l)
Accept equilibrium signs in equations.
Award [1 max] if correct equations are given at wrong electrodes.
i
concentration cell has different concentrations of electrolyte «solutions» «but same electrodes and electrolytes»
OR
standard voltaic cell has different electrodes/electrolytes «but same concentration of electrolytes»
Accept “both half-cells in concentration cell made from same materials”.
ii
«»
(+) 1.19 «V»
3 significant figures needed for mark.
iii
more spontaneous because E > Eθcell
i
photon/«sun»light absorbed by the dye/photosensitizer/«transition» metal complex
OR
dye/photosensitizer/«transition» metal complex excited by photon/«sun»light
electron«s» move«s» to conduction band
OR
electron«s» transferred to semiconductor/TiO2
ii
I3− + 2e− → 3I− «at cathode»
OR
triiodide ions/I3− reduced into/produce iodide ions/I− «at cathode»
iodide ions/I− reduce dye/act as reducing agent AND oxidized into/produce triiodide ions/I3−
OR
dye+ + e− → dye AND 3I- → I3− + 2e−