| Date | November 2015 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 15N.3.SL.TZ0.14 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | Time zone 0 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 14 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
This question is about determining the distance to a nearby star.
Two photographs of the night sky are taken, one six months after the other. When the photographs are compared, one star appears to have shifted from position A to position B, relative to the other stars.
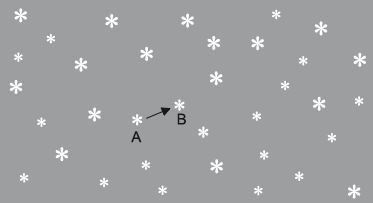
The observed angular displacement of the star is \(\theta \) and the diameter of the Earth’s orbit is \(d\). The distance from the Earth to the star is \(D\).
Outline why the star appears to have shifted from position A to position B.
Draw a diagram showing \(d\), \(D\) and \(\theta \).
Explain the relationship between \(d\), \(D\) and \(\theta \).
One consistent set of units for \(D\) and \(\theta \) are parsecs and arc-seconds. State one other consistent set of units for this pair of quantities.
Suggest whether the distance from Earth to this star can be determined using spectroscopic parallax.
Markscheme
the star is (much) closer than the other star (and close enough to Earth) / parallax effect has been observed;
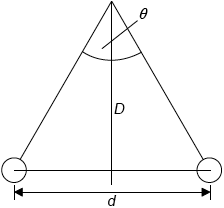
Award [1] if all three (d, D, \(\theta \)) are shown correctly.
Do not allow d shown as the radius.
Accept D as a line from Earth to the star.
\(\sin \frac{\theta }{2} = \frac{d}{{2D}}\) or \(\tan \frac{\theta }{2} = \frac{d}{{2D}}\) or \(\theta = \frac{d}{D}\);
consistent explanation, eg: small angle of approximation yields \(\theta = \frac{d}{D}\);
Allow ECF from (b)(i), eg: if d shown as radius.
any angular unit quoted for \(\theta \) and any linear unit quoted for \(D\);
(yes) star is close enough (in local galaxy) to determine spectral characteristics;
Note: not the same question as HL.
Examiners report
Well discriminating question, better candidates realized that the star is closer to Earth and drew the diagram. Many candidates made a mistake to present diameter and the angle, giving half of the proper values. The relationships were generally well explained. In the alternative pair of quantities many candidates stated only the quantity for distance, not for the angle. The HL question related to Hubble’s law was properly answered only by better candidates. The SL question was poorly answered with most confusing stellar and spectroscopic parallax.
Well discriminating question, better candidates realized that the star is closer to Earth and drew the diagram. Many candidates made a mistake to present diameter and the angle, giving half of the proper values. The relationships were generally well explained. In the alternative pair of quantities many candidates stated only the quantity for distance, not for the angle. The HL question related to Hubble’s law was properly answered only by better candidates. The SL question was poorly answered with most confusing stellar and spectroscopic parallax.
Well discriminating question, better candidates realized that the star is closer to Earth and drew the diagram. Many candidates made a mistake to present diameter and the angle, giving half of the proper values. The relationships were generally well explained. In the alternative pair of quantities many candidates stated only the quantity for distance, not for the angle. The HL question related to Hubble’s law was properly answered only by better candidates. The SL question was poorly answered with most confusing stellar and spectroscopic parallax.
Well discriminating question, better candidates realized that the star is closer to Earth and drew the diagram. Many candidates made a mistake to present diameter and the angle, giving half of the proper values. The relationships were generally well explained. In the alternative pair of quantities many candidates stated only the quantity for distance, not for the angle. The HL question related to Hubble’s law was properly answered only by better candidates. The SL question was poorly answered with most confusing stellar and spectroscopic parallax.
Well discriminating question, better candidates realized that the star is closer to Earth and drew the diagram. Many candidates made a mistake to present diameter and the angle, giving half of the proper values. The relationships were generally well explained. In the alternative pair of quantities many candidates stated only the quantity for distance, not for the angle. The HL question related to Hubble’s law was properly answered only by better candidates. The SL question was poorly answered with most confusing stellar and spectroscopic parallax.

