| Date | May 2015 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 15M.1.HL.TZ1.9 |
| Level | Higher level | Paper | Paper 1 | Time zone | Time zone 1 |
| Command term | Question number | 9 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A fixed mass of an ideal gas undergoes an isochoric (isovolumetric) change. This increases the pressure of the gas. Which describes the change of internal energy of the gas and the direction of transfer of thermal energy?
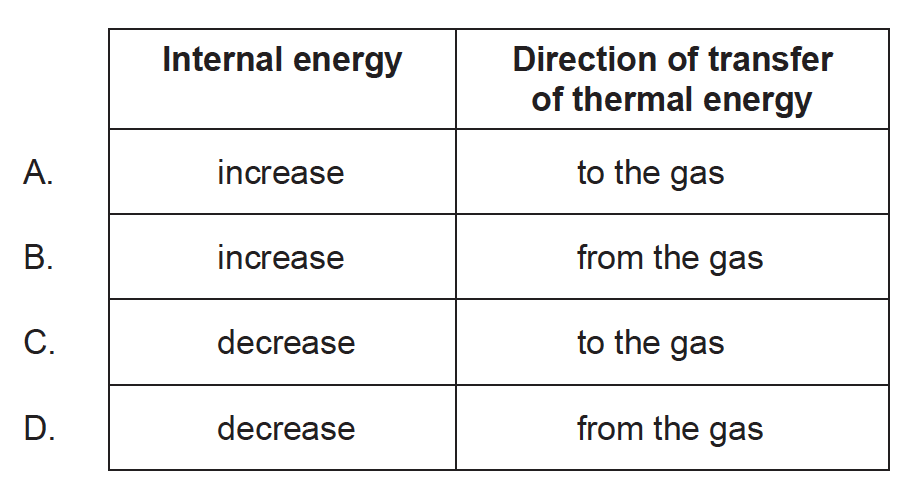
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
[N/A]
Syllabus sections
Show 43 related questions
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.9: What does the constant n represent in the equation of state for an ideal gas pV = nRT? A....
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.11: Under what conditions of pressure and temperature does a real gas approximate to an ideal gas?
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.12: Unpolarized light of intensity I0 is incident on a polarizing filter. Light from this filter...
- 17M.3.SL.TZ1.1d: The cross-sectional area of the tube is 1.3 × 10–3\(\,\)m2 and the temperature of air is 300...
- 17M.3.SL.TZ1.1c: Outline how the results of this experiment are consistent with the ideal gas law at constant...
- 17M.3.SL.TZ1.1a: The student measured the height H of the air column and the corresponding air pressure p....
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.5c.ii: The experiment was carried out at a temperature of 18 °C. The volume of cylinder B was 1.3...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ2.4c: Rutherford and Royds expected 2.7 x 1015 alpha particles to be emitted during the experiment....
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.10: An ideal gas has a volume of 15 ml, a temperature of 20 °C and a pressure of 100 kPa. The...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.12: A sealed container contains a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen gas.The...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.15: Two pulses are travelling towards each other. What is a possible pulse shape when the...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.12: A fixed mass of an ideal gas in a closed container with a movable piston initially occupies...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.11: A thin-walled cylinder of weight W, open at both ends, rests on a flat surface. The cylinder...
- 16N.2.HL.TZ0.3b: 0.46 mole of an ideal monatomic gas is trapped in a cylinder. The gas has a volume of 21 m3...
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.12: The pressure of a fixed mass of an ideal gas in a container is decreased at constant...
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.11: An ideal gas of N molecules is maintained at a constant pressure p. The graph shows how the...
- 16M.1.SL.TZ0.12: Under what conditions of density and pressure is a real gas best described by the equation of...
- 16M.1.SL.TZ0.11: Which of the following is not an assumption of the kinetic model of ideal gases? A. All...
- 15M.1.SL.TZ1.11: In the kinetic model of an ideal gas, which of the following is not assumed? A. The...
- 15M.1.HL.TZ1.8: A fixed mass of an ideal gas has a constant volume. Two quantities, R and S, of the gas vary...
- 15M.1.SL.TZ1.9: What is the definition of the mole? A. The amount of substance that has the same mass as...
- 15M.1.SL.TZ2.11: Which of the following is an assumption of the kinetic model of an ideal gas? A. The gas is...
- 14M.1.SL.TZ2.12: An ideal gas is contained in a thermally insulated cylinder by a freely moving piston. The...
- 14M.1.HL.TZ2.11: Two containers, X and Y, are each filled by an ideal gas at the same temperature. The volume...
- 15N.1.HL.TZ0.8: An ideal gas and a solid of the same substance are at the same temperature. The average...
- 14N.1.HL.TZ0.8: What are the conditions of temperature and pressure at which the behaviour of a real gas...
- 11N.1.HL.TZ0.12: A fixed mass of an ideal gas is at temperature T. The pressure is doubled and the volume is...
- 11M.1.SL.TZ2.11: The volume of an ideal gas in a...
- 11M.1.SL.TZ2.9: The energy of the molecules of an ideal gas...
- 13M.2.HL.TZ1.12b: The graph shows how the pressure P of a sample of a fixed mass of an ideal gas varies with...
- 12M.2.SL.TZ2.4b: Argon behaves as an ideal gas for a large range of temperatures and pressures. One mole of...
- 12M.2.SL.TZ2.4c: At the temperature of 350 K, the piston in (b) is now freed and the argon expands until its...
- 12M.2.SL.TZ2.4a: State two assumptions of the kinetic model of an ideal gas.
- 11M.2.SL.TZ2.3b: Describe, with reference to the energy of the molecules, the difference in...
- 11M.2.SL.TZ2.3c: A piece of iron is placed in a kiln until it reaches the temperature θ of...
- 13N.2.HL.TZ0.4a: Describe how the ideal gas constant R is defined.
- 13N.2.HL.TZ0.4b: Calculate the temperature of 0.100 mol of an ideal gas kept in a cylinder of volume 1.40×10–3...
- 09M.1.SL.TZ1.11: In the kinetic model of an ideal gas, it is assumed that A. the forces between the...
- 10M.1.HL.TZ1.13: The behaviour of a monatomic gas such as helium will approximate to that of an ideal gas when...
- 10N.1.SL.TZ0.11: Which of the following is an assumption made in the kinetic model of ideal gases? A. ...
- 10N.1.HL.TZ0.11: The graph shows the variation with absolute temperature \(T\) of the pressure \(p\) of a...
- 10M.1.SL.TZ1.10: The mole is defined as A. \(\frac{1}{{12}}\) the mass of an atom of the isotope...
- 09N.1.HL.TZ0.12: The behaviour of real gases is different from that predicted for ideal gases. Which of the...

