| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.1.HL.TZ2.26 |
| Level | Higher level | Paper | Paper 1 | Time zone | Time zone 2 |
| Command term | Question number | 26 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A beam of monochromatic light is incident on a diffraction grating of N lines per unit length. The angle between the first orders is θ1.
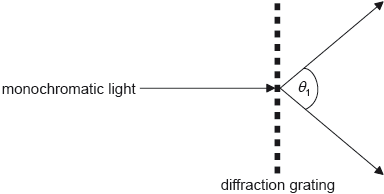
What is the wavelength of the light?
A. \(\frac{{\sin {\theta _1}}}{N}\)
B. N sin θ1
C. N sin\(\left( {\frac{{{\theta _1}}}{2}} \right)\)
D. \(\frac{{\sin \left( {\frac{{{\theta _1}}}{2}} \right)}}{N}\)
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
[N/A]
Syllabus sections
Show 64 related questions
- 18M.2.HL.TZ2.5c: The slit separation is increased. Outline one change observed on the screen.
- 18M.2.HL.TZ2.5b: Monochromatic light from a single source is incident on two thin, parallel slits. The...
- 18M.2.HL.TZ2.5a: Monochromatic light from two identical lamps arrives on a screen. ...
- 18M.2.HL.TZ1.3b.ii: Deduce, in mm, the width of one slit.
- 18M.2.HL.TZ1.3b.i: Calculate the angular separation between the central peak and the missing peak in the...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.28: Monochromatic light is incident on 4 rectangular, parallel slits. The first principal maximum...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.27: Monochromatic light of wavelength λ in air is incident normally on a thin film of refractive...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.i: State and explain the differences between the pattern on the screen due to the grating and...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.ii: The distance from the centre of the pattern to A is 4.1 x 10–2 m. The distance from the...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.i: Explain why zero intensity is observed at position A.
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.29: A transparent liquid forms a parallel-sided thin film in air. The diagram shows a ray I...
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.28: Monochromatic light is incident on two identical slits to produce an interference pattern...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.ii: Suggest the variation in the output voltage from the light sensor that will be observed as...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.i: Determine the width of one of the slits.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.27: Blue light is incident on two narrow slits. Constructive interference takes place along...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.27: For fringes to be observed in a double-slit interference experiment, the slits must emit...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.28: Light of wavelength λ is incident normally on a diffraction grating that has a slit...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.27: Monochromatic light is incident on a double slit. Both slits have a finite width. The light...
- 16M.1.HL.TZ0.35: Which of the following...
- 16M.1.HL.TZ0.23: In a double-slit interference experiment, the following...
- 15M.3.HL.TZ1.13b: The following data are available: Refractive index of oil = 1.4Refractive index of water =...
- 15M.3.HL.TZ1.13a: Outline the process by which coloured fringes are formed.
- 15M.3.SL.TZ2.21a: Explain why an interference pattern is produced on the screen.
- 15M.3.SL.TZ2.21b: The two slits are separated by 2.2 mm and the distance from the slits to the screen is 1.8 m....
- 15N.3.HL.TZ0.11a: Calculate the wavelength of the light within the soap solution.
- 15N.3.HL.TZ0.11b: Calculate the minimum thickness of the soap film that results in constructive interference...
- 15N.3.HL.TZ0.11c: Without a calculation, explain why a soap film that is twice as thick as that calculated in...
- 14M.3.HL.TZ1.13a: Calculate the wavelength of the light.
- 14M.3.HL.TZ1.13b: The upper glass plate is now replaced with a curved glass plate. The dotted line represents...
- 14N.1.HL.TZ0.16: Radiation is incident on a single rectangular slit. The diffracted beam that emerges from the...
- 14N.3.HL.TZ0.15b: When white light is normally incident on the surface of the oil, the film appears green to an...
- 14N.3.HL.TZ0.15a: Explain why the film of oil appears to show coloured fringes.
- 14M.3.HL.TZ2.14a: Determine the minimum thickness of the oil layer that gives rise to the least amount of light...
- 14M.3.HL.TZ2.14b: Describe the change in the intensity of the reflected light as the thickness of the oil layer...
- 14M.3.SL.TZ2.19a: Outline what is meant by the term (i) coherent. (ii) monochromatic.
- 14M.3.SL.TZ2.19c: (i) Show that the laser produces light of wavelength equal to 720 nm. (ii) State the...
- 14M.3.SL.TZ2.19b: State the phase difference between the light waves from the two slits that meet at B.
- 13M.1.HL.TZ1.15: A parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength λ passes through a slit of width b and...
- 12M.1.HL.TZ2.18: A coherent beam of light of wavelength λ is incident on a double slit. The width of the slits...
- 13M.3.SL.TZ1.21a: Laser light is monochromatic and coherent. Explain what is meant by (i) monochromatic. (ii)...
- 13M.3.SL.TZ1.12c: The number of lines per millimetre in the diffraction grating in (b) is reduced. Describe the...
- 13M.3.SL.TZ1.21b: A beam of laser light is incident normally on a diffraction grating which has 600 lines per...
- 13M.3.HL.TZ1.13a: State what phase change occurs on reflection at the air-coating boundary and at...
- 13M.3.HL.TZ1.13b: The thickness d of the coating layer is 110 nm. Determine the wavelength for which there is...
- 13M.3.HL.TZ2.14a: A ray of monochromatic light is incident on a thin film of soap water that is suspended in...
- 13M.3.HL.TZ2.14b: White light is incident normally on the soap film. The thickness d of the soap film is 225 nm...
- 12N.3.SL.TZ0.20a: State the condition necessary to observe interference between two light sources.
- 11N.3.HL.TZ0.10b: State and explain how the fringe separation changes if the angle of the wedge is increased...
- 11N.3.SL.TZ0.17b: The number of slits is now increased. State and explain the effect, if any, this has on the...
- 11N.3.HL.TZ0.10a: Outline how the fringes are formed.
- 12N.3.SL.TZ0.20b: The diagram below shows an arrangement for observing a double slit interference pattern. A...
- 12N.3.SL.TZ0.20c: The slits in (b) are replaced by a large number of slits of the same width and separation as...
- 12M.3.SL.TZ2.19b: Suggest why, even though there are dark fringes in the pattern, no energy is lost.
- 12M.3.HL.TZ2.12a: Show that when θ=0 the condition for destructive interference between rays X and Y...
- 12M.3.HL.TZ2.12b: Light of wavelength 640 nm in air is incident normally on the glass surface. (i) Show that...
- 13N.3.HL.TZ0.11a: An observer viewing the microscope slide at near-normal incidence measures the fringe spacing...
- 11M.3.SL.TZ1.21a: Determine the angular separation of the two lines when viewed in the second order spectrum.
- 11M.3.SL.TZ1.21b: State why it is more difficult to observe the double yellow line when viewed in the...
- 11M.3.HL.TZ1.15a: Deduce that the thickness of the air wedge t that gives rise to a bright fringe, is given by...
- 11M.3.HL.TZ1.15b: The length of the air wedge, L, is 8.2 cm. The bright fringes are each separated by...
- 10N.3.HL.TZ0.G5a: State why the light reflected from the two microscope slides produces a system of...
- 10N.3.HL.TZ0.G5b: The condition that a bright fringe is observed in the field of view of the travelling...
- 10N.3.HL.TZ0.G5c: In the diagram, the length of the slides is 5.00 cm. The wavelength of the monochromatic...
- 10N.3.SL.TZ0.G3b: For a particular grating, the distance between adjacent slits is...

