| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.2.SL.TZ2.6 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 2 | Time zone | Time zone 2 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 6 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Rhodium-106 (\(_{\,\,\,45}^{106}{\text{Rh}}\)) decays into palladium-106 (\(_{\,\,\,46}^{106}{\text{Pd}}\)) by beta minus (β–) decay.
The binding energy per nucleon of rhodium is 8.521 MeV and that of palladium is 8.550 MeV.
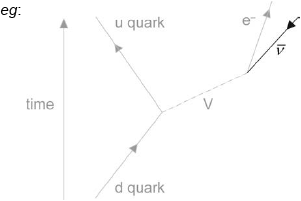
β– decay is described by the following incomplete Feynman diagram.
Rutherford constructed a model of the atom based on the results of the alpha particle scattering experiment. Describe this model.
State what is meant by the binding energy of a nucleus.
Show that the energy released in the β– decay of rhodium is about 3 MeV.
Draw a labelled arrow to complete the Feynman diagram.
Identify particle V.
Markscheme
«most of» the mass of the atom is confined within a very small volume/nucleus
«all» the positive charge is confined within a very small volume/nucleus
electrons orbit the nucleus «in circular orbits»
[2 marks]
the energy needed to separate the nucleons of a nucleus
OR
energy released when a nucleus is formed from its nucleons
Allow neutrons AND protons for nucleons
Don’t allow constituent parts
[1 mark]
Q = 106 × 8.550 − 106 × 8.521 = 3.07 «MeV»
«Q ≈ 3 Me V»
[1 mark]
line with arrow as shown labelled anti-neutrino/\(\bar v\)
Correct direction of the “arrow” is essential
The line drawn must be “upwards” from the vertex in the time direction i.e. above the horizontal
[1 mark]
V = W–
[1 mark]

