| Date | November 2012 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 12N.1.sl.TZ0.22 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 1 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Question number | 22 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Which row correctly describes \({\text{1.0 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ NaOH(aq)}}\)?
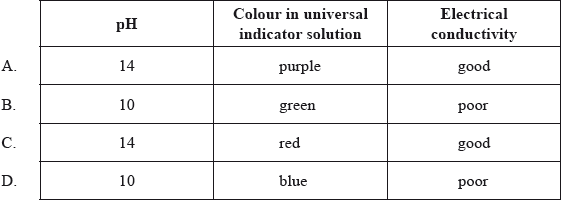
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
There was concern expressed that we expect candidates to know the colours of universal indicator by rote learning. Far from it, we would expect candidates to have absorbed this information during regular lab classes and demonstrations.
Syllabus sections
Show 53 related questions
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.5c: A student working in the laboratory classified HNO3, H2SO4, H3PO4 and HClO4 as acids based on...
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.5b.iii: State the conjugate base of the hydroxide ion, OH–.
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.5b.ii: State what is meant by the term conjugate base.
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.5b.i: Identify two different amphiprotic species in the above reactions.
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.7b.i: Calculate the amount, in mol, of NaOH(aq) used.
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.ii: Identify one conjugate acid-base pair in the reaction.
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.i: Identify the amphiprotic species.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.20: Which of the following is correct? A. A weak acid is a proton donor and its aqueous...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.26: Which species acts as a Lewis and Brønsted–Lowry base? A. [Al(H2O)6]3+ B. BF3 C....
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.24: Which species produced by the successive dissociations of phosphoric acid, H3PO4,...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.19: Which is an acid-base conjugate pair? A. H3O+ / OH– B. H2SO4 / SO42– C. ...
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.19: Which species behave as Brønsted–Lowry bases in the following reaction? H2SO4 + HNO3...
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.1b: Phosphine is usually prepared by heating white phosphorus, one of the allotropes of...
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.1a: (i) Draw a Lewis (electron dot) structure of phosphine. (ii) State the hybridization of the...
- 16M.2.sl.TZ0.1b: Phosphine is usually prepared by heating white phosphorus, one of the allotropes of...
- 16M.1.sl.TZ0.19: Which is a...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.2c: Predict and explain the pH of the following aqueous solutions, using equations to support...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.8d.i: State the formula of the conjugate base of chloroethanoic acid,...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.7e.ii: Define the term weak base according to the Brønsted–Lowry theory.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.6e: Explain whether BF3 can act as a Brønsted-Lowry acid, a Lewis acid or both.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.5f.ii: Define the term weak base according to the Brønsted-Lowry theory.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.5f.iii: Deduce the formulas of conjugate acid-base pairs in the reaction...
- 14M.1.hl.TZ2.26: What is the conjugate base of phenol,...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ1.21: Which are acid-base pairs according to the Brønsted‒Lowry theory? I. ...
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.9g: Describe what is meant by a weak Brønsted-Lowry base, including an equation for the reaction...
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.6d.iv: State the formula of the conjugate base of...
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.25: What are the conjugate acid–base pairs in the following...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.7b.ii: Explain the behaviour of HF in terms of the Brønsted–Lowry theory of acids.
- 13N.1.sl.TZ0.21: What are the conjugate acid–base pairs in the following...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.5c.i: Define a Brønsted–Lowry acid.
- 13M.1.hl.TZ2.26: Which of the following is an example of a Lewis acid–base reaction, but not a Brønsted–Lowry...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.6b.i: Define an acid according to the Brønsted–Lowry theory and the Lewis...
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.5b.i: Define an acid according to the Brønsted–Lowry and Lewis theories. Brønsted–Lowry...
- 10N.2.hl.TZ0.7d: The reaction between \({{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{(aq)}}\) and...
- 10N.1.sl.TZ0.21: What is the conjugate base of \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)...
- 09N.1.hl.TZ0.24: According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory, how does each species act in the equilibrium...
- 09N.1.sl.TZ0.22: What is the formula of the conjugate base of the hydrogenphosphate ion,...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.i: For each of the reactions A and B, deduce whether water is acting as an acid or a base and...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.3b.iii: State an equation, including state symbols, for the reaction of ethanoic acid with water....
- 10M.1.sl.TZ2.22: Which species behave as Brønsted-Lowry acids in the following reversible...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.6c.i: Define a Brønsted-Lowry acid.
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.6c.ii: Deduce the two acids and their conjugate bases in the following...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ2.21: Which are definitions of an acid according to the Brønsted-Lowry and Lewis theories?
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.1b.vii: The other product of the reaction is ethanoic acid,...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.8a.i: Define the terms acid and base according to the Brønsted-Lowry theory. Distinguish between a...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.22: Consider the equilibrium...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.5c.i: Define the terms acid and base according to the Brønsted-Lowry theory and state one example...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ2.20: Which is not a conjugate acid-base pair? A. \({\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\) and...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.5a.v: Explain, using the Brønsted-Lowry theory, how water can act either as an acid or a base. In...
- 12M.1.sl.TZ2.21: What is the Brønsted–Lowry conjugate base of \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{PO}}_4^ -...
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.i: State the equation for the reaction of ammonia with water.
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.ii: Explain why ammonia can act as a Brønsted–Lowry base.
- 11N.1.sl.TZ0.21: Which descriptions are correct for both a Brønsted–Lowry acid and a Lewis acid?

