| Date | November 2013 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 13N.3.hl.TZ0.16 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Outline | Question number | 16 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
There is some concern that increased use of the recreational drug khat is causing social problems.
The structures of two substances found in khat are shown below.
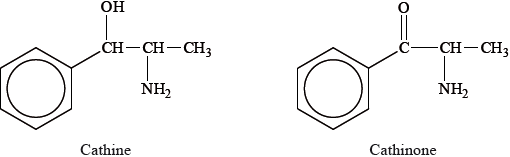
Cathine and cathinone are both classed as sympathomimetic drugs.
Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) is an optical isomer of cathine used in cough medicines.
Outline how PPA and not cathine could be synthesized from the same non-chiral starting materials. Details of reagents and conditions are not required.
Explain why this is the generally preferred method for the synthesis of optically active drugs.
Suggest how the aqueous solubility of cathine or PPA could be increased to facilitate its distribution around the body.
Markscheme
chiral auxiliary/optically active species is used;
that can be connected to a molecule / to make it optically active;
auxiliary creates stereochemical condition necessary to follow a certain pathway / forms (only) one enantiomer / OWTTE;
chiral auxiliary removed to obtain (desired) product;
other methods produce racemic mixture;
enantiomers difficult to separate because they have same physical properties (except rotation of the plane of plane polarised light);
optical isomers might have different physiological activities/(usually) only one is useful/half product is not used;
add acid/\({{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}}\) (to form ionic compound) / converted to its salt;
Examiners report
Option D was a popular option. The identification of the wavenumber range used in the determination of ethanol lead to many correct answers. However, why the absorption range 3200-3600 \({\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 1}}\) is not used still eludes a substantial number of candidates. How the transmission of IR radiation changes with increased levels of ethanol was not answered well, showing a poor understanding of transmittance. The question on the mild analgesic was not very well except for being able to identify the amide group in the molecules in question. The physiological effect of the drug as well as the reason for some drugs being less effective when taken orally was both very well answered. The ‘mix and split’ approach to combinatorial chemistry was generally not done well with answers that were weak showing shallow understanding.
The two structural features found in the sympathomimetic drugs were mostly correctly identified. Although many students were able to identify two chiral centers in the two structures given, not as many could identify the three needed for the mark. In the preferred method for the synthesis of optically active drugs, where many scored full marks but the difficulty of separating enantiomers due to their similar physical properties was the least popular explanation given. Surprisingly, the suggestion for increasing the aqueous solubility of an alkaline drug by adding an acid or converting it to its salt was done poorly showing a lack of understanding of acid-base chemistry and bonding.
In one argument for and one against the legalization of cannabis, while many candidates scored at least one mark out of two, some journalistic answers were seen. Description of the bonding changes that occur when the anti-cancer drug cisplatin attaches to the DNA chain was typically not well answered questions with many candidates being able to provide only one of the two ideas, usually the missing one was that \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }\) leave \({\text{Pt/P}}{{\text{t}}^{2 + }}\). Why the trans-cisplatin is ineffective in the treatment of cancer elicited fewer correct answers than expected. Question 18 was not on AIDS per se but rather on why viral infections are more difficult to treat than bacterial infections. A significant number of students scored part marks thus illustrating shallow understanding and deserves further attention in class. Very often marks were lost due to incomplete arguments.
Option D was a popular option. The identification of the wavenumber range used in the determination of ethanol lead to many correct answers. However, why the absorption range 3200-3600 \({\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 1}}\) is not used still eludes a substantial number of candidates. How the transmission of IR radiation changes with increased levels of ethanol was not answered well, showing a poor understanding of transmittance. The question on the mild analgesic was not very well except for being able to identify the amide group in the molecules in question. The physiological effect of the drug as well as the reason for some drugs being less effective when taken orally was both very well answered. The ‘mix and split’ approach to combinatorial chemistry was generally not done well with answers that were weak showing shallow understanding.
The two structural features found in the sympathomimetic drugs were mostly correctly identified. Although many students were able to identify two chiral centers in the two structures given, not as many could identify the three needed for the mark. In the preferred method for the synthesis of optically active drugs, where many scored full marks but the difficulty of separating enantiomers due to their similar physical properties was the least popular explanation given. Surprisingly, the suggestion for increasing the aqueous solubility of an alkaline drug by adding an acid or converting it to its salt was done poorly showing a lack of understanding of acid-base chemistry and bonding.
In one argument for and one against the legalization of cannabis, while many candidates scored at least one mark out of two, some journalistic answers were seen. Description of the bonding changes that occur when the anti-cancer drug cisplatin attaches to the DNA chain was typically not well answered questions with many candidates being able to provide only one of the two ideas, usually the missing one was that \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }\) leave \({\text{Pt/P}}{{\text{t}}^{2 + }}\). Why the trans-cisplatin is ineffective in the treatment of cancer elicited fewer correct answers than expected. Question 18 was not on AIDS per se but rather on why viral infections are more difficult to treat than bacterial infections. A significant number of students scored part marks thus illustrating shallow understanding and deserves further attention in class. Very often marks were lost due to incomplete arguments.
Option D was a popular option. The identification of the wavenumber range used in the determination of ethanol lead to many correct answers. However, why the absorption range 3200-3600 \({\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 1}}\) is not used still eludes a substantial number of candidates. How the transmission of IR radiation changes with increased levels of ethanol was not answered well, showing a poor understanding of transmittance. The question on the mild analgesic was not very well except for being able to identify the amide group in the molecules in question. The physiological effect of the drug as well as the reason for some drugs being less effective when taken orally was both very well answered. The ‘mix and split’ approach to combinatorial chemistry was generally not done well with answers that were weak showing shallow understanding.
The two structural features found in the sympathomimetic drugs were mostly correctly identified. Although many students were able to identify two chiral centers in the two structures given, not as many could identify the three needed for the mark. In the preferred method for the synthesis of optically active drugs, where many scored full marks but the difficulty of separating enantiomers due to their similar physical properties was the least popular explanation given. Surprisingly, the suggestion for increasing the aqueous solubility of an alkaline drug by adding an acid or converting it to its salt was done poorly showing a lack of understanding of acid-base chemistry and bonding.
In one argument for and one against the legalization of cannabis, while many candidates scored at least one mark out of two, some journalistic answers were seen. Description of the bonding changes that occur when the anti-cancer drug cisplatin attaches to the DNA chain was typically not well answered questions with many candidates being able to provide only one of the two ideas, usually the missing one was that \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }\) leave \({\text{Pt/P}}{{\text{t}}^{2 + }}\). Why the trans-cisplatin is ineffective in the treatment of cancer elicited fewer correct answers than expected. Question 18 was not on AIDS per se but rather on why viral infections are more difficult to treat than bacterial infections. A significant number of students scored part marks thus illustrating shallow understanding and deserves further attention in class. Very often marks were lost due to incomplete arguments.

