| Date | May 2012 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 12M.3.sl.TZ1.C2 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Compare | Question number | C2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Fuel cells and rechargeable batteries are both convenient ways of providing portable electric power.
Compare fuel cells and rechargeable batteries giving one similarity and one difference.
Similarity:
Difference:
One common type of rechargeable cell is the nickel–cadmium (NiCad) battery. For each terminal of this battery state the initial and final oxidation number of the element when the cell is delivering a current. Hence deduce which electrode is acting as the anode and which the cathode.

A common type of fuel cell uses hydrogen and oxygen with an acidic electrolyte. State the half-equations for the reactions at the two electrodes.
Positive electrode:
Negative electrode:
The electrodes of fuel cells and rechargeable batteries have a feature in common with heterogeneous catalysts. Identify this feature and state why it is important for them to work efficiently.
Markscheme
Similarity:
both turn chemical energy into electrical energy / use chemical reactions to produce electricity/lectrical energy / OWTTE;
Difference [1 max]:
rechargeable batteries have reversible reactions but fuel cells do not;
fuel cells consume fuel but rechargeable batteries do not require (external) fuel;
rechargeable batteries can be recharged by electricity but fuel cells cannot;
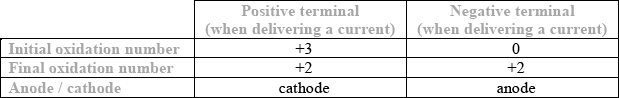
All correct [3], 4 or 5 correct [2], 2 or 3 correct [1]
Positive electrode:
\({{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{4}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{4}}{{\text{e}}^ - } \to {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\);
Negative electrode:
\({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{e}}^ - }\);
large surface area;
changes only occur on the surface / where electron transfer occurs / OWTTE;
Examiners report
Some candidates were able to write one similarity and one difference between fuel cells and rechargeable batteries.
Part (b) was very poorly answered.
None of the candidates scored full marks particularly in part (c) where it was rare to see any correct half-equations; the candidates also overlooked the fact that the electrolyte was acidic.
Part (d) seldom had any correct answers.

