| Date | November 2013 | Marks available | 4 | Reference code | 13N.2.sl.2 |
| Level | SL only | Paper | 2 | Time zone | |
| Command term | Describe and Identify | Question number | 2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The diagram shows two transport processes that operate in a river channel.
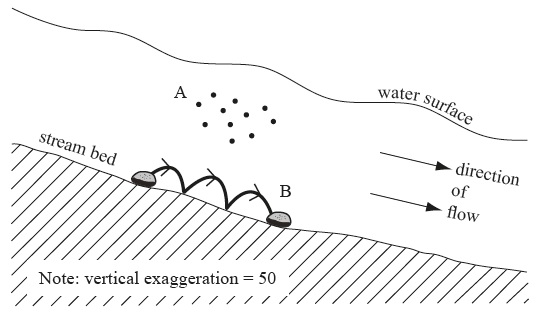
Identify and describe process A and process B shown in the diagram.
Draw a labelled diagram to show the main input, outputs, transfers and stores of the hydrological cycle for an un-vegetated drainage basin.
“Of all the impacts of agriculture on water quality, salinization is the most damaging.” Discuss this statement.
Markscheme
A – Suspension [1 mark] – finer load carried along in the channel above the bed [1 mark].
B – Saltation [1 mark] – coarser material bounces along the river bed [1 mark].
- Input: precipitation [1 mark].
- Outputs: evaporation/run-off/river discharge [1 mark].
- Transfers: must have at least four for two marks (or two for one mark): infiltration, throughflow, overland flow, groundwater flow/base-flow [2 marks].
- Stores: must have at least four for two marks (or two for one mark): atmosphere, soil, groundwater/water table, lakes, river water, surface store/surface depression, snow, water tanks/water butts [2 marks].
Either a systems diagram or a pictorial image of a drainage basin is acceptable.
Award up to a maximum of [3 marks] if there is no diagram.
Responses should show an understanding of salinization and its effects. Salinization is widespread in arid and semi-arid environments where groundwater extraction in coastal areas leads to saline incursion; salt water drawn upwards by capillary action results in salt enrichment of the soil/surface. Irrigation is another cause as, over time, levels of salt build up through repeated watering – leaching of the salts by flooding can lower water quality in rivers. Local geology can also play an important role in some contexts. Salinization damages livelihoods for farmers by limiting agriculture/reducing yields.
As the counter-argument, responses could also examine the impacts of agro-chemicals, sedimentation due to increased run-off, the effects of animal wastes, groundwater pollution and eutrophication of rivers, streams, lakes and/or wetlands where relevant. (Not all of these are required.)
Good answers may question who or what is damaged (land, incomes, ecosystems, local businesses), and should recognize it is a more serious concern in some parts of the world than in others.
Responses that are mainly descriptive and/or look only at salinization should not progress above band D.
At bands E and F responses should discuss the relative importance of at least one other agricultural impact on water quality. At band F there should be a well balanced evaluation.
Marks should be allocated according to the markbands.

