| Date | November 2011 | Marks available | 6 | Reference code | 11N.2.bp.1 |
| Level | SL and HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | 1 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The diagram shows a river floodplain.
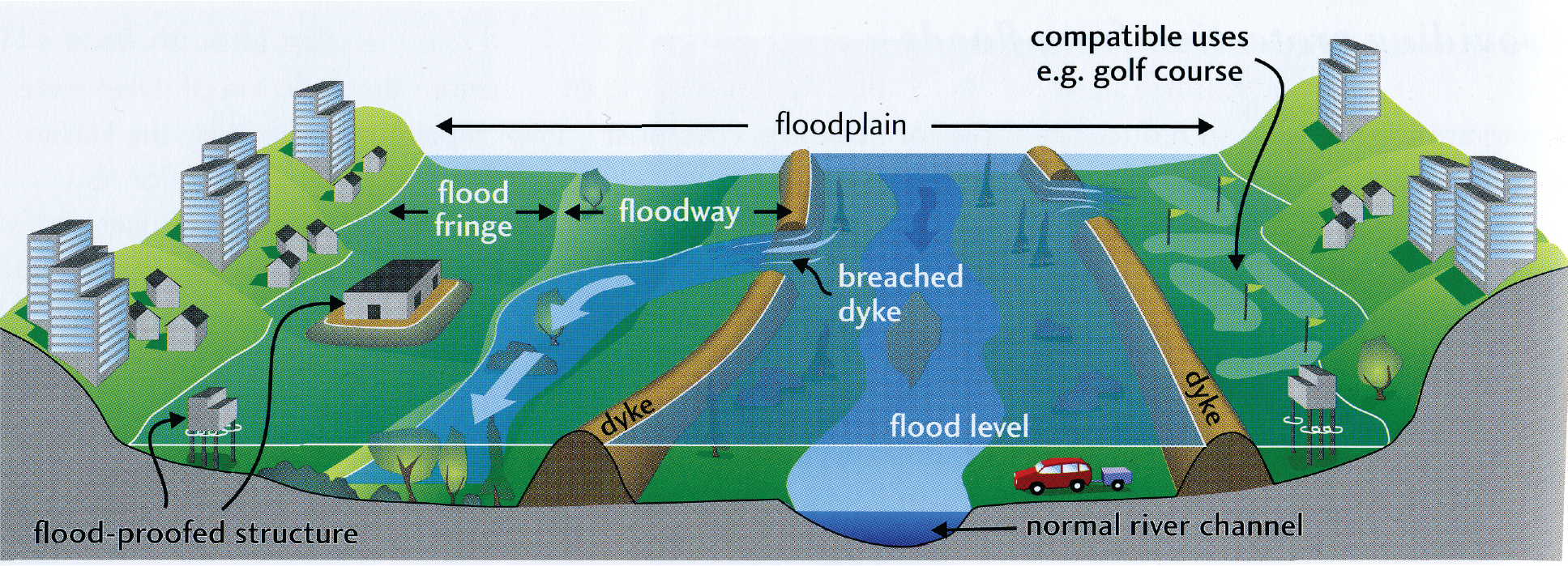
[Source: John Clague and Bob Turner, (2003), Vancouver, City on the Edge, Tricouni Press, page 74]
Referring to the diagram, briefly describe two floodplain management strategies.
Explain how human activities on a floodplain can increase the probability of flooding.
“Eutrophication is the most damaging agricultural impact on water quality.” Discuss this statement.
Markscheme
The diagram provides evidence for several floodplain management strategies, including floodplain zoning; construction and maintenance of dykes; maintenance of a floodway to channel flood waters away from settlements or valuable land; deliberate “set-aside” of floodplain as an area where no development is permitted; flood-proofing of buildings.
Award 1 mark for each valid suggestion for a management strategy, and a further 1 mark in each case for further description or development. Some reference to the diagram is essential for the awarding of the full 4 marks.
Answers could refer to two human activities in detail or several in less detail. Human activities might include: urbanization, mechanized farming causing soil compaction, deforestation, removal of pastureland for arable farming, construction of artificial levees, straightening of the channel, removal of wetlands.
A simple list with no explanation should not be awarded more than 2 marks. A list with some explanation should be credited more than 2 marks where appropriate.
Answers should describe how eutrophication can be caused by farming and how it impacts on water quality. It is expected that answers will examine other impacts of agriculture on water quality and compare these with the impact of eutrophication. This might include the effects of irrigation such as salinization, or the accumulation of toxins/pesticides in water bodies as well as increased water sediment content due to soil erosion following intense precipitation or exposure to wind.
To access bands E and F, answers should include a clear evaluation of one or more agricultural impacts compared to eutrophication.
Marks should be allocated according to the markbands.
Examiners report
Knowledge and understanding was reasonable though at standard level strategies were often identified but not well described with regard to their functioning.
This question proved harder, with few recognizing the importance of "probability". Although human activities were identified, answers rarely explained fully how they might affect flooding
Many discussions were strong on eutrophication, but less convincing on salinization or other impacts, so that at both levels arguments tended to unbalanced. Weaker candidates tended to write about water pollution in general.

