 Any relationship containing powers of \(y\) or \(x\), or an operator other than an addition or multiplication of a constant, will not be a straight line. These are non-linear graphs.
Any relationship containing powers of \(y\) or \(x\), or an operator other than an addition or multiplication of a constant, will not be a straight line. These are non-linear graphs.
Key Concepts
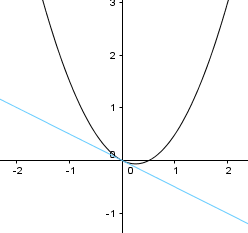
 Parabola
Parabola
The \(x\) term is squared.

 Inverse proportion
Inverse proportion
The axes act as asymptotes, which means the graph does not cross them:
\(y = {1 \over x}\)

 Sinousoidal graphs
Sinousoidal graphs
Periodic functions in which a pattern repeats over time (\(\sin x\) or \(\cos x\)).
 Exponential
Exponential
The rate of change is proportional to the current value (more of this in Capacitors and Nuclear Decay).
HINT: Do not use the term 'exponential' to describe any increasing gradient - it is only true in special cases.

Exponential decay graphs can be distinguished from inversely proportional graphs as they have a finite value at time zero, meaning that they cross the vertical axis. In equal times, the quantity falls by an equal ratio.
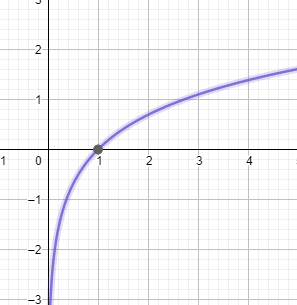
 Logarithmic
Logarithmic
The inverse of an exponential relationship.
How much of Non-linear graphs have you understood?






 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn