DP Mathematics: Applications and Interpretation Questionbank

AHL 1.13—Polar and Euler form
Description
Directly related questions
-
21M.3.AHL.TZ1.1h.i:
Write down and in exponential form, with a constant modulus.
-
21M.3.AHL.TZ1.1h.iii:
Find, in hours, the shortest time from sunrise to sunset at point that is predicted by this model.
-
21M.3.AHL.TZ1.1h.ii:
Hence or otherwise find an equation for in the form , where .
-
EXN.1.AHL.TZ0.14a:
Write down in exponential form.
-
EXN.1.AHL.TZ0.14b:
An equilateral triangle is to be drawn on the Argand plane with one of the vertices at the point corresponding to and all the vertices equidistant from .
Find the points that correspond to the other two vertices. Give your answers in Cartesian form.
-
21M.1.AHL.TZ1.9a.i:
.
-
21M.1.AHL.TZ1.9a.ii:
.
-
21M.1.AHL.TZ1.9b:
Describe these two transformations and give the order in which they are applied.
-
21M.1.AHL.TZ1.9c:
Hence, or otherwise, find the value of when .
-
21M.1.AHL.TZ2.12a.ii:
Find the value of for .
-
21M.1.AHL.TZ2.12a.i:
Find the value of .
-
21M.1.AHL.TZ2.12b:
Find the least value of such that .
-
21N.2.AHL.TZ0.5b.ii:
Hence find in the form , where and .
-
21N.2.AHL.TZ0.5a.ii:
Express in the form , where , giving the exact value of and the exact value of .
-
21N.2.AHL.TZ0.5c.ii:
Find the phase shift of .
-
21N.2.AHL.TZ0.5b.i:
Find in the form .
-
21N.2.AHL.TZ0.5c.i:
Find the maximum value of .
-
21N.2.AHL.TZ0.5a.i:
Plot the position of on an Argand Diagram.
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ1.10a.ii:
.
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ1.10a.i:
.
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ1.10a.iii:
.
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ1.10b.i:
Find this value of .
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ1.10b.ii:
For this value of , plot the approximate position of on the Argand diagram.
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ2.13a:
Find an expression for in the form , where and are real constants.
-
22M.1.AHL.TZ2.13b:
Hence write down the maximum voltage in the circuit.
-
SPM.1.AHL.TZ0.15a.i:
find the values of , , and .
-
SPM.1.AHL.TZ0.15a.ii:
draw , , , and on the following Argand diagram.
-
SPM.1.AHL.TZ0.15b:
Let .
Find the value of for which successive powers of lie on a circle.
-
18M.1.AHL.TZ1.H_11a.i:
Express w2 and w3 in modulus-argument form.
-
18M.1.AHL.TZ1.H_11a.ii:
Sketch on an Argand diagram the points represented by w0 , w1 , w2 and w3.
-
18M.1.AHL.TZ1.H_11b:
Show that the area of the quadrilateral Q is .
-
18M.1.AHL.TZ1.H_11c:
Let . The points represented on an Argand diagram by form the vertices of a polygon .
Show that the area of the polygon can be expressed in the form , where .
-
17M.1.AHL.TZ1.H_2a.i:
By expressing and in modulus-argument form write down the modulus of ;
-
17M.1.AHL.TZ1.H_2a.ii:
By expressing and in modulus-argument form write down the argument of .
-
17M.1.AHL.TZ1.H_2b:
Find the smallest positive integer value of , such that is a real number.
-
19M.2.AHL.TZ1.H_6a:
Show the points represented by and on the following Argand diagram.
-
17M.1.AHL.TZ2.H_11a:
Solve .
-
17M.1.AHL.TZ2.H_11b:
Show that .
-
17M.1.AHL.TZ2.H_11c.i:
Find the modulus and argument of in terms of . Express each answer in its simplest form.
-
17M.1.AHL.TZ2.H_11c.ii:
Hence find the cube roots of in modulus-argument form.
-
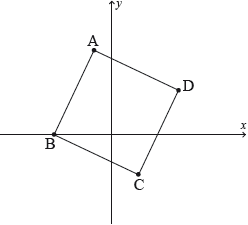
17M.1.AHL.TZ2.H_5:
In the following Argand diagram the point A represents the complex number and the point B represents the complex number . The shape of ABCD is a square. Determine the complex numbers represented by the points C and D.