| Date | November 2017 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 17N.1.HL.TZ0.7 |
| Level | Higher level | Paper | Paper 1 | Time zone | 0 - no time zone |
| Command term | Question number | 7 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A toy car of mass 0.15 kg accelerates from a speed of 10 cm s–1 to a speed of 15 cm s–1. What is the impulse acting on the car?
A. 7.5 mN s
B. 37.5 mN s
C. 0.75 N s
D. 3.75 N s
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.7: A stopper of mass 8 g leaves the opening of a container that contains pressurized gas.The...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ1.6: Child X throws a ball to child Y. The system consists of the ball, the children and the...
- 22M.2.SL.TZ1.1a: Outline two differences between the momentum of the box and the momentum of the load at the...
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.9: Two objects m1 and m2 approach each other along a straight line with speeds v1 and v2 as...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.1b.ii:
Show that the tension in the rope is about 5 kN.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.7: A cyclist accelerates in a straight line. At one instant, when the cyclist is exerting a...
- 22M.1.HL.TZ1.9: Two bodies each of equal mass travelling in opposite directions collide head-on. What is a...
- 22M.1.SL.TZ1.9: Two trolleys of equal mass travel in opposite directions as shown. The trolleys collide...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.1e:
A second identical ball is placed at the bottom of the bowl and the first ball is displaced so that its height from the horizontal is equal to 8.0 m.
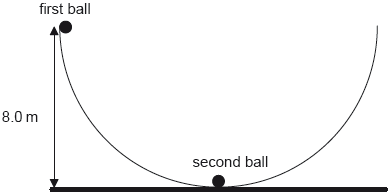
The first ball is released and eventually strikes the second ball. The two balls remain in contact. Determine, in m, the maximum height reached by the two balls.
-
16N.1.SL.TZ0.8:
A ball of mass m strikes a vertical wall with a speed v at an angle of θ to the wall. The ball rebounds at the same speed and angle. What is the change in the magnitude of the momentum of the ball?
A. 2 mv sin θ
B. 2 mv cos θ
C. 2 mv
D. zero - 19M.2.HL.TZ1.6b.ii: Show that the collision is inelastic.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1c.i:
between A and B.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1c.ii:
between B and C.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.15: Two pulses are travelling towards each other. What is a possible pulse shape when the...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ1.1d.i: Calculate the impulse required from the net to stop the skier and state an appropriate unit...
-
18N.1.SL.TZ0.9:
A ball of mass m collides with a wall and bounces back in a straight line. The ball loses 75 % of the initial energy during the collision. The speed before the collision is v.
What is the magnitude of the impulse on the ball by the wall?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 18N.2.SL.TZ0.3b: Explain why the egg is likely to break when dropped onto concrete from the same height.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.3a: Define impulse.
-
18N.2.SL.TZ0.1a:
Determine the initial acceleration of the spacecraft.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.1a:
Determine the initial acceleration of the spacecraft.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.iii: Explain why the egg is likely to break when dropped onto concrete from the same height.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.6: A block rests on a frictionless horizontal surface. An air rifle pellet is fired horizontally...
-
18M.2.SL.TZ1.1c.i:
between A and B.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.6: The graph shows the variation of momentum with time for an object. What net force acts on...
- 19M.2.SL.TZ1.5a: Calculate the speed of the combined masses immediately after the collision.
- 19M.1.SL.TZ2.8: A table-tennis ball of mass 3 g is fired with a speed of 10 m s-1 from a stationary toy gun...
-
19N.2.SL.TZ0.1a:
Calculate the speed of the ball as it leaves the racket.
-
17N.2.SL.TZ0.1d:
The girl chooses to jump so that she lands on loosely-packed snow rather than frozen ice. Outline why she chooses to land on the snow.
- 21N.1.SL.TZ0.9: A ball rolls on the floor towards a wall and rebounds with the same speed and at the...
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.5: An object, initially at rest, is accelerated by a constant force. Which graphs show the...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.8: A net force acts on a body. Which characteristic of the body will definitely change? A....
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.ii:
The egg comes to rest in a time of 55 ms. Determine the magnitude of the average decelerating force that the ground exerts on the egg.
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.8: A moving system undergoes an explosion. What is correct for the momentum of the system and...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.6b.i: Calculate the speed of the combined masses immediately after the collision.
-
17M.2.SL.TZ1.1d.ii:
Explain, with reference to change in momentum, why a flexible safety net is less likely to harm the skier than a rigid barrier.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.9: An inelastic collision occurs between two bodies in the absence of external forces. What...
-
19N.2.SL.TZ0.1b:
Show that the average force exerted on the ball by the racket is about 50 N.
-
18M.2.SL.TZ1.1c.ii:
between B and C.
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.5: The graph shows the variation with time t of the force F acting on an object of mass 15 000...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.6: A ball of mass m is thrown with an initial speed of u at an angle θ to the horizontal as...
-
18M.2.SL.TZ2.1d:
A second identical ball is placed at the bottom of the bowl and the first ball is displaced so that its height from the horizontal is equal to 8.0 m.

The first ball is released and eventually strikes the second ball. The two balls remain in contact. Determine, in m, the maximum height reached by the two balls.
-
22M.2.SL.TZ2.1b.ii:
Show that the tension in the rope is about 5 kN.
-
18M.2.SL.TZ1.1b.i:
Determine the magnitude of the average resultant force acting on the block between B and C.
-
19N.2.SL.TZ0.7b(ii):
Calculate the ratio .
-
20N.1.SL.TZ0.3:
An object of mass moving at velocity collides with a stationary object of mass . The objects stick together after the collision. What is the final speed and the change in total kinetic energy immediately after the collision?
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1b.i:
Determine the magnitude of the average resultant force acting on the block between B and C.
-
20N.1.SL.TZ0.9:
An object of mass strikes a vertical wall horizontally at speed . The object rebounds from the wall horizontally at speed .
What is the magnitude of the change in the momentum of the object?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.1.SL.TZ1.9:
An object is moving in a straight line. A force F and a resistive force f act on the object along the straight line.
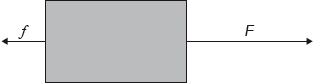
Both forces act for a time t.
What is the rate of change of momentum with time of the object during time t ?
A. F + f
B. F – f
C. (F + f )t
D. (F – f )t
-
20N.2.SL.TZ0.1a(iii):
Determine . State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.6: Masses X and Y rest on a smooth horizontal surface and are connected by a massless spring....
- 21M.1.SL.TZ1.6: A ball undergoes an elastic collision with a vertical wall. Which of the following is equal...
- 21M.1.SL.TZ1.9: An electron has a linear momentum of 4.0 × 10−25 kg m s−1. What is the order of magnitude...
- 21M.1.SL.TZ2.8: A projectile is launched upwards at an angle θ to the horizontal with an initial momentum p0...
- 21M.1.SL.TZ2.7: Two identical blocks, each of mass m and speed v, travel towards each other on a frictionless...
-
19M.2.SL.TZ2.1ai:
Calculate the average force exerted by the racquet on the ball.
-
21M.2.SL.TZ2.1a:
The player’s foot is in contact with the ball for 55 ms. Calculate the average force that acts on the ball due to the football player.
-
17N.2.SL.TZ0.1c:
When the sledge is moving on the horizontal region of the snow, the girl jumps off the sledge. The girl has no horizontal velocity after the jump. The velocity of the sledge immediately after the girl jumps off is 4.2 m s–1. The mass of the girl is 55 kg and the mass of the sledge is 5.5 kg. Calculate the speed of the sledge immediately before the girl jumps from it.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.1ai:
Calculate the average force exerted by the racquet on the ball.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.1a(iii):
Determine . State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.7:
A stationary nucleus of polonium-210 undergoes alpha decay to form lead-206. The initial speed of the alpha particle is v. What is the speed of the lead-206 nucleus?
A. v
B. v
C. v
D. v
-
18N.2.SL.TZ0.3a:
Determine the magnitude of the average decelerating force that the ground exerts on the egg.
-
21M.2.SL.TZ1.1d.ii:
Player B intercepts the ball when it is at its peak height. Player B holds a paddle (racket) stationary and vertical. The ball is in contact with the paddle for 0.010 s. Assume the collision is elastic.
Calculate the average force exerted by the ball on the paddle. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
- 19M.2.SL.TZ1.5b: Show that the collision is inelastic.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.9: A ball of mass 0.2 kg strikes a force sensor and sticks to it. Just before impact the ball is...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.7:
A ball of mass m collides with a vertical wall with an initial horizontal speed u and rebounds with a horizontal speed v. The graph shows the variation of the speed of the ball with time.
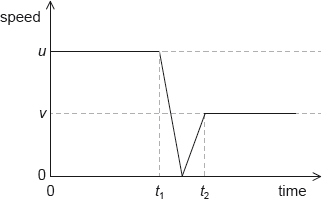
What is the magnitude of the mean net force on the ball during the collision?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21N.2.SL.TZ0.1d.i:
Determine the average force exerted on the floor by the ball.
- 21N.2.SL.TZ0.1d.ii: Suggest why the momentum of the ball was not conserved during the collision with the floor.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.1a:
Outline why a force acts on the airboat due to the fan blade.
-
22M.2.SL.TZ2.1a:
Outline why a force acts on the airboat due to the fan blade.

