| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.2.hl.TZ2.2 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Formulate | Question number | 2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Graphing is an important tool in the study of rates of chemical reactions.
The graph represents the titration of 25.00 cm3 of 0.100 mol dm−3 aqueous ethanoic acid with 0.100 mol dm−3 aqueous sodium hydroxide.
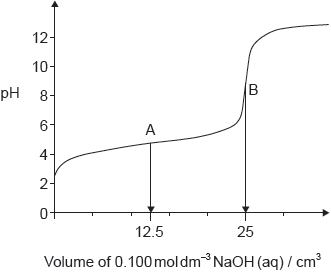
Deduce the major species, other than water and sodium ions, present at points A and B during the titration.
Calculate the pH of 0.100 mol dm−3 aqueous ethanoic acid.
Ka = 1.74 × 10−5
Outline, using an equation, why sodium ethanoate is basic.
Predict whether the pH of an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride will be greater than, equal to or less than 7 at 298 K.
Formulate the equation for the reaction of nitrogen dioxide, NO2, with water to form two acids.
Formulate the equation for the reaction of one of the acids produced in (e)(i) with calcium carbonate.
Markscheme
A: CH3COOH/ethanoic/acetic acid AND CH3COO–/ethanoate/acetate ions
B: CH3COO–/ethanoate/acetate ions
Penalize “sodium ethanoate/acetate” instead of “ethanoate/acetate ions” only once.
[2 marks]
OR
[H+] = 1.32 × 10–3 «mol dm–3»
«pH =» 2.88
Accept [2] for correct final answer.
[2 marks]
«forms weak acid and strong base, thus basic»
CH3COO–(aq) + H2O(l) CH3COOH(aq) + OH–(aq)
Accept → for .
[1 mark]
less than 7
[1 mark]
2NO2(g) + H2O(l) → HNO2(aq) + HNO3(aq)
[1 mark]
2HNO2(aq) + CaCO3(s) → Ca(NO2)2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
OR
2HNO3(aq) + CaCO3(s) → Ca(NO3)2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
[1 mark]

