| Date | May 2017 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 17M.3.SL.TZ1.7 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | Time zone 1 |
| Command term | Calculate | Question number | 7 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
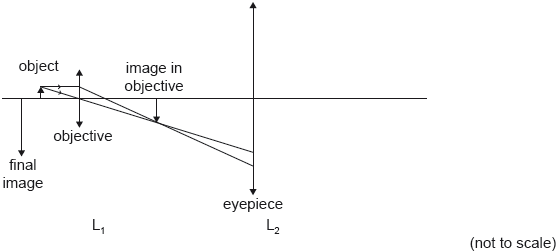
The diagram is a partially-completed ray diagram for a compound microscope that consists of two thin converging lenses. The objective lens L1 has a focal length of 3.0 cm. The object is placed 4.0 cm to the left of L1. The final virtual image is formed at the near point of the observer, a distance of 24 cm from the eyepiece lens L2.
Two converging lenses are used to make an astronomical telescope. The focal length of the objective is 85.0 cm and that of the eyepiece is 2.50 cm. The telescope is used to form a final image of the Moon at infinity.
State what is meant by a virtual image.
Show that the image of the object formed by L1 is 12 cm to the right of L1.
The distance between the lenses is 18 cm. Determine the focal length of L2.
On the diagram draw rays to locate the focal point of L2. Label this point F.
Explain why, for the final image to form at infinity, the distance between the lenses must be 87.5 cm.
The angular diameter of the Moon at the naked eye is 7.8 × 10–3 rad.
Calculate the angular diameter of the final image of the Moon.
By reference to chromatic aberration, explain one advantage of a reflecting telescope over a refracting telescope.
Markscheme
an image formed by extensions of rays, not rays themselves
OR
an image that cannot be projected on a screen
[1 mark]
\(\frac{1}{v} = \frac{1}{{3.0}} - \frac{1}{{4.0}}\)
«v = 12 cm»
[1 mark]
u = 18 – 12 = 6.0 «cm»
v = –24 «cm»
«\(\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{{6.0}} - \frac{1}{{24}} \Rightarrow \)» f = 8.0 «cm»
Award [2 max] for answer of 4.8 cm.
Minus sign required for MP2.
[3 marks]
line parallel to principal axis from intermediate image meeting eyepiece lens at P
line from arrow of final image to P intersecting principal axis at F
[2 marks]
object is far away so intermediate image forms at focal plane of objective
for final image at infinity object must also be at focal point of eyepiece
«hence 87.5 cm»
No mark for simple addition of focal lengths without explanation.
[2 marks]
angular magnification = \(\frac{{85.0}}{{2.50}}\) = 34
angular diameter 3.4 × 7.8 × 10−3 = 0.2652 ≈ 0.27 «rad»
[2 marks]
chromatic aberration is the dependence of refractive index on wavelength
but mirrors rely on reflection
OR
mirrors do not involve refraction
«so do not suffer chromatic aberration»
[2 marks]

