| Date | May 2015 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 15M.3.sl.TZ2.18 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Describe | Question number | 18 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Diseases may be caused by bacteria or viruses.
Explain how penicillins work as antibacterials.
The R group in the general structure of penicillin shown below represents a side-chain which is regularly modified.
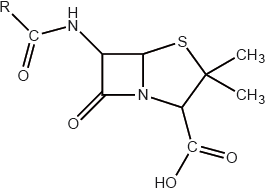
Explain why this modification is necessary.
Describe two ways in which antiviral drugs work.
Markscheme
prevent the formation of bacterial cell walls / interfere with chemicals/enzyme/transpeptidase needed by bacteria to form normal cell walls / inhibits cross-links developing in bacterial cell walls;
(osmosis) causes water to enter bacterial cell and cell bursts / cell wall weakens (making it more permeable to water) and bacterium bursts (and dies);
makes penicillin more effective / makes penicillin resistant to penicillinase (enzyme) / allows different methods of administration / penicillins can be made which are resistant to acid in the stomach;
change cell membrane to prevent viruses entering/attaching to cell;
alter cell’s genetic material so virus cannot use it to multiply;
inhibit enzymes involved in replication/reverse transcriptase / stop enzyme activity inside the cell (and prevent the viruses from multiplying);
prevent replicated virus leaving the cell;
initiates apoptosis/death of cells infected by viruses;
mimic guanosine/base-sugar monomer in DNA/RNA formation inhibiting enzymes involved in replication;
Examiners report
Many students were able to explain how penicillins work as antibacterial agents although sometimes the answers lacked clarity. The reason for the modification of the side-chain of penicillin was often linked to bacterial resistance but did not specifically address how it actually affects the action of penicillin. Candidates were often unclear on the different ways that anti-viral drugs can work and although they usually managed to achieve one of the two marks, many explanations lacked the precision in terms of their mode of action.
Many students were able to explain how penicillins work as antibacterial agents although sometimes the answers lacked clarity. The reason for the modification of the side-chain of penicillin was often linked to bacterial resistance but did not specifically address how it actually affects the action of penicillin. Candidates were often unclear on the different ways that anti-viral drugs can work and although they usually managed to achieve one of the two marks, many explanations lacked the precision in terms of their mode of action.
Many students were able to explain how penicillins work as antibacterial agents although sometimes the answers lacked clarity. The reason for the modification of the side-chain of penicillin was often linked to bacterial resistance but did not specifically address how it actually affects the action of penicillin. Candidates were often unclear on the different ways that anti-viral drugs can work and although they usually managed to achieve one of the two marks, many explanations lacked the precision in terms of their mode of action.

