| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.3.hl.TZ1.5 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Outline | Question number | 5 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Aluminium is produced by the electrolysis of a molten electrolyte containing bauxite.
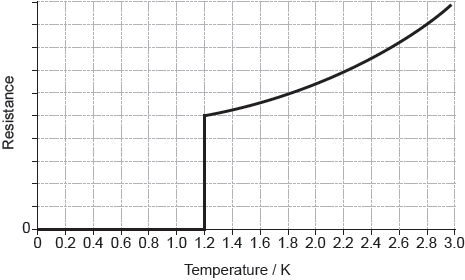
The graph of the resistance of aluminium with temperature is shown below.
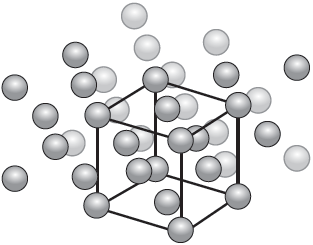
The diagram illustrates the crystal structure of aluminium metal with the unit cell indicated. Outline the significance of the unit cell.
When X-rays of wavelength 0.154 nm are directed at a crystal of aluminium, the first order diffraction pattern is observed at 18°. Determine the separation of layers of aluminium atoms in the crystal, in m, using section 1 of the data booklet.
Deduce what the shape of the graph indicates about aluminium.
Outline why the resistance of aluminium increases above 1.2 K.
The concentration of aluminium in drinking water can be reduced by precipitating aluminium hydroxide. Calculate the maximum concentration of aluminium ions in water of pH 7 at 298 K. Solubility product of aluminium hydroxide = 3.3 × 10−34 at 298 K.
Markscheme
the smallest repeating unit «from which the crystal structure can be derived»
Accept “building block that the structure is made from”.
[1 mark]
«nλ = 2d sin θ»
1 × 1.54 × 10–10 = 2 × d × sin 18
d «\(\frac{{1.54 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}{\text{ m}}}}{{2 \times 0.309}}\)» = 2.49 × 10–10 «m»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
[2 marks]
type 1
superconductor
[2 marks]
collisions between electrons and «lattice of metal» ions become more frequent
OR
thermal oscillations/vibrations disrupt the Cooper electron pairs
[1 mark]
Ksp = [Al3+][OH–]3 «= 3.3 × 10–34»
[Al3] = «\(\frac{{3.3 \times {{10}^{ - 34}}}}{{{{(1 \times {{10}^{ - 7}})}^3}}} = \)» 3.3 × 10–13 «mol dm–3»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
[2 marks]

