| Date | May 2017 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 17M.3.hl.TZ2.5 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Compare and contrast | Question number | 5 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Rhodium and palladium are often used together in catalytic converters. Rhodium is a good reduction catalyst whereas palladium is a good oxidation catalyst.
Nickel(II) ions are least soluble at pH 10.5. Calculate the molar solubility of nickel(II) hydroxide at this pH. KspNi(OH)2 = 5.48 × 10–16.
Rhodium is paramagnetic with an electron configuration of [Kr] 5s14d8.
Explain, in terms of electron spin pairing, why paramagnetic substances are attracted to a magnetic field and diamagnetic substances are not.
Rhodium is a type 1 superconductor.
Sketch graphs of resistance against temperature for a conductor and superconductor.
Contrast type 1 and type 2 superconductors by referring to three differences between them.
Markscheme
Ksp= [Ni2+][OH−]2
OR
5.48 x 10−16 = [Ni2+][10−3.5]2
«[Ni2+] =» 5.48 x 10−9 «mol dm−3»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
[2 marks]
paramagnetic materials have unpaired electrons
OR
diamagnetic materials have all electrons «spin-»paired
unpaired electrons align with an external magnetic field
OR
paired electrons are not influenced by magnetic field
Accept “diamagnetic materials have no unpaired electrons" for M1.
[2 marks]
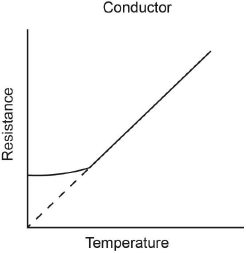
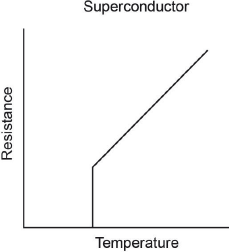
Conductor:
Accept any concave upwards curve or line showing resistance increasing with temperature. There should be a
y-axis intercept. Do not accept x-axis intercept for conductor.
Superconductor:
Sharp transition with vertical line to x-axis. Greater than Tc, accept any concave upwards curve or line showing resistance increasing with temperature.
[2 marks]
Any three of:
type 1 have lower critical temperature/Tc «than type 2»
OR
type 2 can superconduct at higher temperatures «than type 1»
type 1 are «elemental» metals AND type 2 can be alloys/composites/metal oxide ceramics/perovskites
type 1 have sharp transition to superconductivity AND type 2 have more gradual transition
type 1 have all «magnetic» flux expelled to normal state AND type 2 have partial penetration of flux in mixed state
type 1 typically work via Cooper pairs AND type 2 may not necessarily use this mechanism
magnetic fields can penetrate type 2 in the mixed state «in a type of Vortex» AND type 1 has no mixed state
type 1 have one critical magnetic field/Bc AND type 2 have two/Bc1 and Bc2
Award [1 max] if three correct pieces of information are given for one type only without contrasting with the other type.
Marks may also be awarded from suitable sketch(es).
Accept “H” for “B”.
[3 marks]

