| Date | November 2013 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 13N.3.SL.TZ0.7 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Compare | Question number | 7 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Trypanosoma brucei is a parasite which causes sleeping sickness. The parasites rely exclusively on glycolysis for energy production. Peptides acting as inhibitors of an enzyme from the glycolytic pathway are being studied as possible drugs to kill the parasite. The glycolytic enzyme triose phosphate isomerase was incubated in the presence of various concentrations of three different peptides and the remaining activity was measured. As a control, the enzyme was incubated without inhibitor peptides.
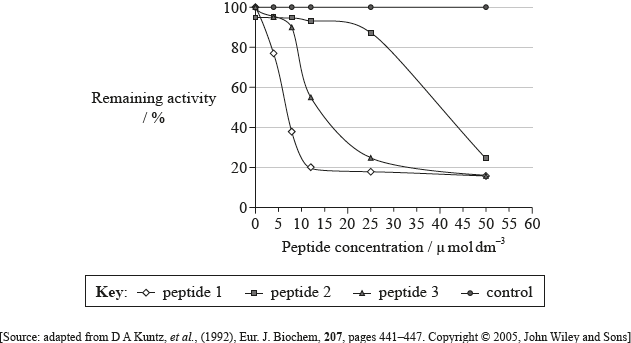
State the remaining activity of triose phosphate isomerase when \({\text{8 }}\mu \,{\text{mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) of peptide 1 is used.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . %
Compare the effect of increasing the concentration of peptide 2 and peptide 3 on the remaining activity.
Identify, with a reason, which of the peptides is the most effective inhibitor of triose phosphate isomerase.
Deduce, with reasons, whether the peptides act as competitive or non-competitive inhibitors of triose phosphate isomerase.
Markscheme
37(%) (allow answer in the range of 34(%) to 38(%))
as the concentration increased the remaining activity decreased in both peptides;
peptide 2 does not cause activity to drop significantly until higher concentration/\({\text{25 }}\mu \,{\text{mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) while peptide 3 causes decrease at low concentrations/\({\text{10 }}\mu \,{\text{mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\);
(enzyme activity of) peptide 2 decrease steadily after \({\text{25 }}\mu \,{\text{mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) while (activity of) peptide 3 shows little change;
peptide 3 more effective than peptide 2 (after conc. of \({\text{10 }}\mu \,{\text{mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\))
peptide 1, only low concentrations needed to inhibit enzyme
non-competitive does not compete for active site / binds to enzyme away from the active site;
peptides 1/3 non-competitive, only small concentrations cause inhibition;
peptide 2 competitive, only inhibits enzyme at higher concentration;
peptide 2 competes with substrate, at higher concentration it joins the active site more readily than the substrate;
Examiners report
Most could read the graph correctly to earn 1 mark. Some were outside the allotted range so candidates do need to be careful and use a ruler for data analysis questions.
Many candidates were able to get one mark for stating that as the concentration of both peptides increased the remaining activity decreased. Few were able to get the second mark as they found it difficult to describe what the graph was showing.
Most were able to correctly identify peptide 1 as the most effective inhibitor because only low concentrations were needed to inhibit enzyme activity.
Very few candidates were able to get any marks for this question.

