| Date | November 2012 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 12N.2.bp.13 |
| Level | SL and HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | |
| Command term | Describe | Question number | 13 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The map shows cities experiencing high or negative growth rates in countries with differing levels of urbanization.
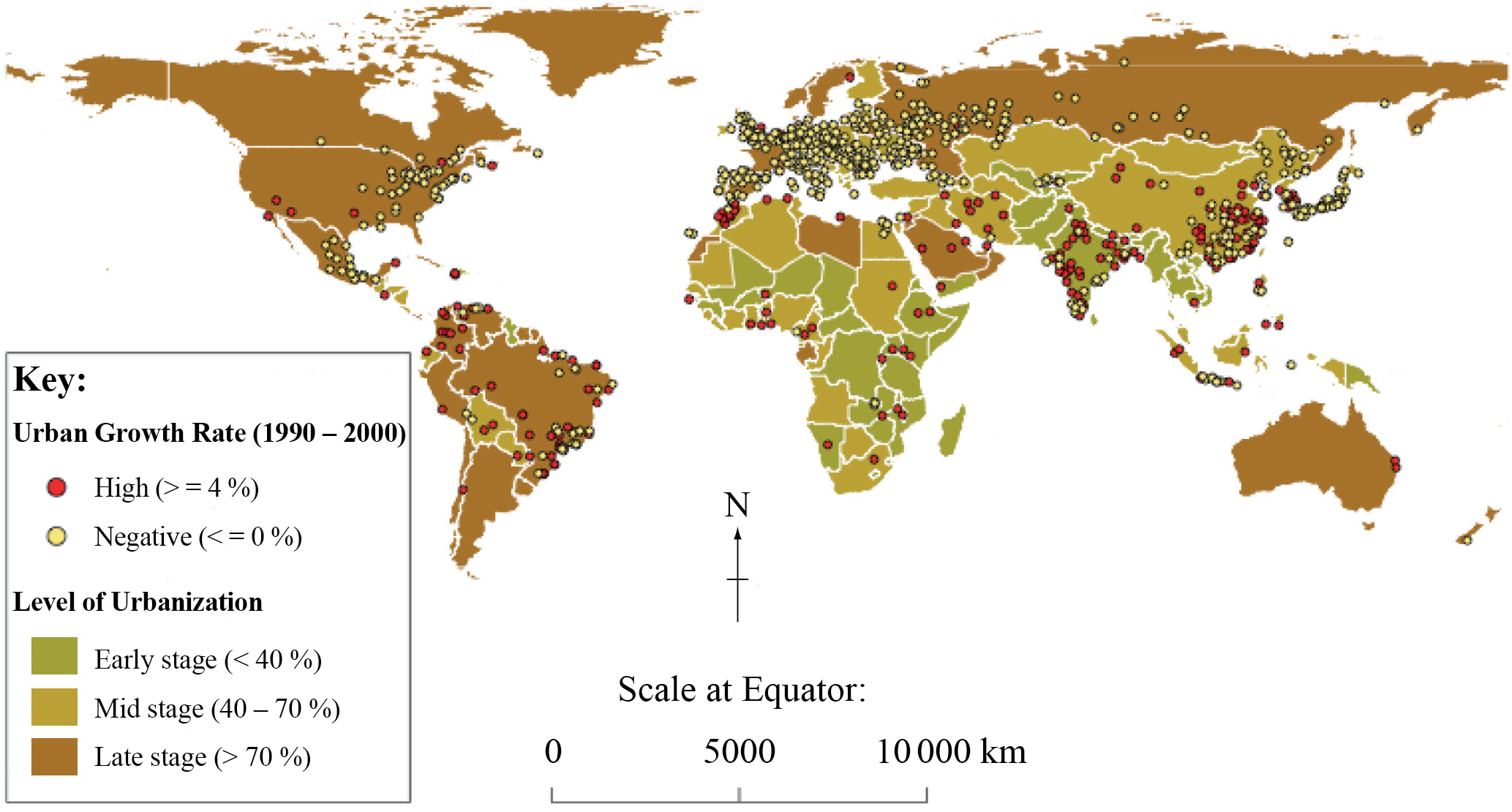
[Source: UN HABITAT Global Urban Observatory]
Identify the two major components of urban growth.
Referring to the map, describe the relationship between the level of urbanization and urban growth rate.
Explain the pull factors associated with counter-urbanization.
Discuss the challenges facing one or more cities experiencing rapid growth.
Markscheme
Natural change [1 mark] and net migration [1 mark].
There may be alternative ways of expressing these two components/processes and these should be credited.
The level of urbanization and urban growth rate show a negative relationship (i.e. cities with high annual growth more likely to be found in countries at an early stage of urbanization or vice versa) [1 mark].
This can be exemplified through mention of specific countries or regions (e.g. the majority of cities with negative growth are found in Europe and North America) [1 mark].
For a third mark, either name or describe an anomaly (e.g. China and Brazil are anomalies because they contain significant numbers of cities with high and negative growth) or provide some quantification (e.g. making use of the urbanization percentages) [1 mark].
Counter-urbanization should be defined as a centrifugal movement / urban-rural movement (there may be other ways of expressing this) [1 mark].
The remaining [4 marks] are available for identifying and explaining the pull factors such as perceived environmental/social quality, housing availability/costs, commuting potential, pursuit of specific employment opportunities, amongst others. Either two factors can be well-explained for full marks or a larger range in less detail.
Answers are expected to identify the negative consequences of high growth rates in urban areas (scale can vary from megacity to smaller cities). Expect references to problems with housing, utilities, services, employment, public health and communication infrastructure. These problems are in turn likely to have economic impacts, as well as environmental impacts.
At bands E and F expect more than a list of problems. The scale of the challenges may be commented on, or the nature of rapid growth making it hard for city authorities to manage the growth successfully (and there may be links with the concept of sustainability).
Marks should be allocated according to the markbands.
Examiners report
This was well attempted though some responses referred to urban area growth rather than population growth.
Well done, with most recognizing the negative correlation and able to provide exemplification and quantification or anomaly.
Some answers concentrated on urban push factors rather than rural pull factors.
Candidates had a good grasp of urban problems in rapidly growing cities and described them well but some could not resist answering with a problem-solution approach and were not always able to state the challenge, such as how to slow down rural-urban migration, or how to improve the quality of housing, simply describing how poor housing (for example, in favelas) was a problem.

