| Date | May 2019 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 19M.2.HL.TZ2.3 |
| Level | Higher level | Paper | Paper 2 | Time zone | 2 |
| Command term | Draw | Question number | 3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The diagram shows the direction of a sound wave travelling in a metal sheet.
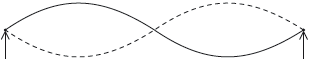
The sound wave in air in (c) enters a pipe that is open at both ends. The diagram shows the displacement, at a particular time T, of the standing wave that is set up in the pipe.
A particular air molecule has its equilibrium position at the point labelled M.
Sound of frequency f = 2500 Hz is emitted from an aircraft that moves with speed v = 280 m s–1 away from a stationary observer. The speed of sound in still air is c = 340 m s–1.
Particle P in the metal sheet performs simple harmonic oscillations. When the displacement of P is 3.2 μm the magnitude of its acceleration is 7.9 m s-2. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of P when its displacement is 2.3 μm.
The wave is incident at point Q on the metal–air boundary. The wave makes an angle of 54° with the normal at Q. The speed of sound in the metal is 6010 m s–1 and the speed of sound in air is 340 m s–1. Calculate the angle between the normal at Q and the direction of the wave in air.
The frequency of the sound wave in the metal is 250 Hz. Determine the wavelength of the wave in air.
On the diagram, at time T, draw an arrow to indicate the acceleration of this molecule.
On the diagram, at time T, label with the letter C a point in the pipe that is at the centre of a compression.
Calculate the frequency heard by the observer.
Calculate the wavelength measured by the observer.
Markscheme
Expression or statement showing acceleration is proportional to displacement ✔
so «» = 5.7«ms–2» ✔
✔
✔
✔
horizontal arrow «at M» pointing left ✔
any point labelled C on the vertical line shown below ✔
eg:
✔
«Hz» ✔
«m» ✔
Examiners report
This was well answered at both levels.
Many scored full marks on this question. Common errors were using the calculator in radian mode or getting the equation upside down.
This was very well answered.
Very few candidates could interpret this situation and most arrows were shown in a vertical plane.
This was answered well at both levels.
This was answered well with the most common mistake being to swap the speed of sound and the speed of the aircraft.
Answered well with ECF often being awarded to those who answered the previous part incorrectly.