| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 18M.3.SL.TZ1.9 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | 1 |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | 9 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A ray of light travelling in an optic fibre undergoes total internal reflection at point P.
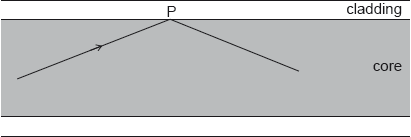
The refractive index of the core is 1.56 and that of the cladding 1.34.
The input signal in the fibre has a power of 15.0 mW and the attenuation per unit length is 1.24 dB km–1.
Calculate the critical angle at the core−cladding boundary.
The use of optical fibres has led to a revolution in communications across the globe. Outline two advantages of optical fibres over electrical conductors for the purpose of data transfer.
Draw on the axes an output signal to illustrate the effect of waveguide dispersion.
Calculate the power of the output signal after the signal has travelled a distance of 3.40 km in the fibre.
Explain how the use of a graded-index fibre will improve the performance of this fibre optic system.
Markscheme
«sin c = »
c = 59.2«°»
Accept values in the range: 59.0 to 59.5.
Accept answer 1.0 rad.
[1 mark]
optic fibres are not susceptible to earthing problems
optic fibres are very thin and so do not require the physical space of electrical cables
optic fibres offer greater security as the lines cannot be tapped
optic fibres are not affected by external electric/magnetic fields/interference
optic fibres have lower attenuation than electrical conductors/require less energy
the bandwidth of an optic fibre is large and so it can carry many communications at once/in a shorter time interval/faster data transfer
[2 marks]
a signal that is wider and lower, not necessarily rectangular, but not a larger area
[1 mark]
attenuation = –1.24 × 3.4 «= –4.216 dB»
–4.216 = 10 log
I = 5.68 «mW»
Need negative attenuation for MP1, may be shown in MP2.
For mp3 answer must be less than 15 mW (even with ECF) to earn mark.
Allow [3] for BCA.
[3 marks]
refractive index near the edge of the core is less than at the centre
speed of rays which are reflected from the cladding are greater than the speed of rays which travel along the centre of the core
the time difference for the rays that reflect from the cladding layer compared to those that travel along the centre of the core is less
OR
the signal will remain more compact/be less spread out/dispersion is lower
bit rate of the system may be greater
[3 marks]