| Date | November 2017 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 17N.1.hl.TZ0.39 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 1 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Question number | 39 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Which compound gives this 1H NMR spectrum?
A. CH3CH2OCH2CH3
B. CH3CH2OH
C. CH3CH2CH3
D. CH3CH2CH2OH
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
-
22M.2.hl.TZ1.6b(iii):
Deduce the number of signals that you would expect in the 1H NMR spectrum of nitrobenzene and the relative areas of these.
- 22M.2.hl.TZ1.6a(iv): State a technique used to determine the length of the bonds between N and O in solid HNO3.
-
17M.1.hl.TZ1.40:
Which technique is used to determine the bond lengths and bond angles of a molecule?
A. X-ray crystallography
B. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy
C. Mass spectroscopy
D. 1H NMR spectroscopy
-
18M.2.hl.TZ2.9a.ii:
Mass spectra A and B of the two isomers are given.
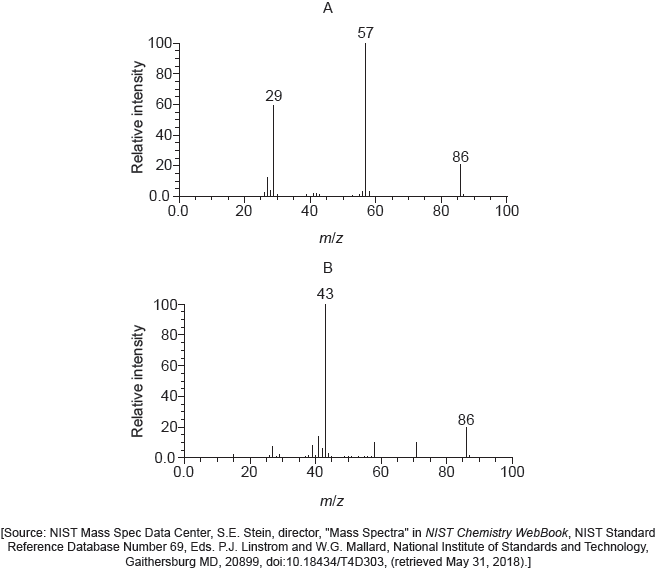
Explain which spectrum is produced by each compound using section 28 of the data booklet.
- 18M.1.hl.TZ1.40: Which would be the most effective method to distinguish between liquid propan-1-ol and...
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.1l.ii:
Predict the splitting pattern of the 1H NMR spectrum of urea.
-
17M.3.hl.TZ2.21c.ii:
Predict the chemical shift and the splitting pattern seen for the hydrogens on the carbon atom circled in the diagram. Use section 27 of the data booklet.
- 18N.1.hl.TZ0.40: Which technique may be used to find the bond lengths and bond angles within a...
- 18N.2.hl.TZ0.8c: Predict the chemical shift and splitting pattern of the signal produced by the hydrogen atoms...
- 16N.2.hl.TZ0.1f: Predict the 1HNMR data for ethanedioic acid and ethane-1,2-diol by completing the table.
-
19M.1.hl.TZ1.40:
Which can be identified using infrared (IR) spectroscopy?
A. functional groups
B. molar mass
C. 3-D configuration
D. bond angle
-
19M.2.hl.TZ2.1c(v):
Deduce the splitting pattern you would expect for the signals in a high resolution 1H NMR spectrum.
2.3 ppm:
9.8 ppm:
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.2a:
Identify the wavenumber of one peak in the IR spectrum of benzoic acid, using section 26 of the data booklet.
-
19M.2.hl.TZ1.2b:
Identify the spectroscopic technique that is used to measure the bond lengths in solid benzoic acid.
-
22M.1.hl.TZ1.38:
Which compound produces the following 1H NMR spectrum?
[Spectral Database for Organic Compounds, SDBS. SDBS Compounds and Spectral Search. [graph] Available at:
https://sdbs.db.aist.go.jp [Accessed 3 January 2019].]
A. propanalB. propanone
C. propane
D. methlypropane
- 17M.1.hl.TZ2.40: Which technique can be used to identify bond length and bond angle? A. 1H NMR...
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.iii:
Suggest the structural formula of this compound.
- 21N.1.hl.TZ0.40: Which substance has the following 1H NMR spectrum? SDBS, National Institute of Advanced...
-
19N.3.hl.TZ0.7:
X-ray crystallography of a metal crystal produces a diffraction pattern of bright spots.
Using X-rays of wavelength 1.54 × 10−10 m, the first bright spots were produced at an angle θ of 22.3° from the centre.
Calculate the separation between planes of atoms in the lattice, in meters, using section 1 of the data booklet.
-
16N.1.hl.TZ0.40:
Which property explains why tetramethylsilane, Si(CH3)4, can be used as a reference standard in 1H NMR spectroscopy?
A. It has a high boiling point.
B. It is a reactive compound.
C. All its protons are in the same chemical environment.
D. It gives multiple signals.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.6b.ii:
Deduce the splitting patterns in the 1H NMR spectrum of C2H5Cl.
-
18M.3.hl.TZ2.27b:
Predict the chemical shifts and integration for each signal in the 1H NMR spectrum for ethanol using section 27 of the data booklet.
-
20N.1.hl.TZ0.40:
Which compound with the molecular formula has this high resolution ?
From: libretexts.org. Courtesy of Chris Schaller, Professor (Chemistry)
at College of Saint Benedict/Saint John’s University.A. but-3-en-2-ol,
B. butanal,
C. butanone,
D. but-3-en-1-ol,
-
19N.1.hl.TZ0.40:
Which is the 1H NMR spectrum of tetramethylsilane, TMS, (CH3)4Si?
-
17M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.i:
Deduce what information can be obtained from the 1H NMR spectrum.
-
17M.2.hl.TZ1.6b.iii:
Explain why tetramethylsilane (TMS) is often used as a reference standard in 1H NMR.
-
20N.2.hl.TZ0.1d(v):
Deduce the number of signals and chemical shifts with splitting patterns in the 1H NMR spectrum of ethoxyethane. Use section 27 of the data booklet.
-
21M.1.hl.TZ1.40:
Which compound produces the following 1H NMR spectrum?
SDBS, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST).
A. PropaneB. Propanone
C. Propanal
D. 2,2-dimethylpropane
- 21M.2.hl.TZ1.1d(ii): State a technique that could be used to determine the crystal structure of the solid compound.
-
18M.2.hl.TZ1.1l.iii:
Outline why TMS (tetramethylsilane) may be added to the sample to carry out 1H NMR spectroscopy and why it is particularly suited to this role.
- 21M.2.hl.TZ1.5b(ii): Deduce the chemical shift of this signal. Use section 27 of the data booklet.
-
21M.1.hl.TZ2.40:
What information can be deduced from the splitting pattern of 1H NMR signals?
A. total number of hydrogen atoms in a compound
B. number of hydrogen atoms on adjacent atom(s)
C. functional group on which hydrogen atoms are located
D. number of hydrogen atoms in a particular chemical environment
-
22M.2.hl.TZ2.8e(ii):
Deduce the splitting pattern in the 1H NMR spectrum for 1-bromopropane.
-
21N.2.hl.TZ0.1d:
Predict the number of 1H NMR signals, and splitting pattern of the –CH3 seen for propanone (CH3COCH3) and propanal (CH3CH2CHO).

