| Date | November 2015 | Marks available | 4 | Reference code | 15N.3ca.hl.TZ0.4 |
| Level | HL only | Paper | Paper 3 Calculus | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Hence and Show that | Question number | 4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Consider the function \(f(x) = \frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}},{\text{ }}x \in \mathbb{R}\).
Illustrate graphically the inequality, \(\frac{1}{5}\sum\limits_{r = 1}^5 {f\left( {\frac{r}{5}} \right) < \int_0^1 {f(x){\text{d}}x < \frac{1}{5}\sum\limits_{r = 0}^4 {f\left( {\frac{r}{5}} \right)} } } \).
Use the inequality in part (a) to find a lower and upper bound for \(\pi \).
Show that \(\sum\limits_{r = 0}^{n - 1} {{{( - 1)}^r}{x^{2r}} = \frac{{1 + {{( - 1)}^{n - 1}}{x^{2n}}}}{{1 + {x^2}}}} \).
Hence show that \(\pi = 4\left( {\sum\limits_{r = 0}^{n - 1} {\frac{{{{( - 1)}^r}}}{{2r + 1}} - {{( - 1)}^{n - 1}}\int_0^1 {\frac{{{x^{2n}}}}{{1 + {x^2}}}{\text{d}}x} } } \right)\).
Markscheme
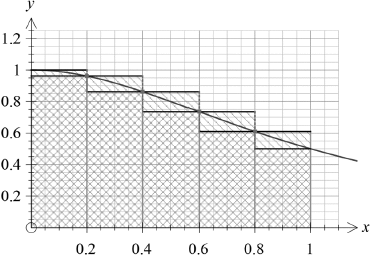 A1A1A1
A1A1A1
A1 for upper rectangles, A1 for lower rectangles, A1 for curve in between with \(0 \le x \le 1\)
hence \(\frac{1}{5}\sum\limits_{r = 1}^5 {f\left( {\frac{r}{5}} \right) < \int_0^1 {f(x){\text{d}}x < \frac{1}{5}\sum\limits_{r = 0}^4 {f\left( {\frac{r}{5}} \right)} } } \) AG
[3 marks]
attempting to integrate from \(0\) to \(1\) (M1)
\(\int_0^1 {f(x){\text{d}}x = [\arctan x]_0^1} \)
\( = \frac{\pi }{4}\) A1
attempt to evaluate either summation (M1)
\(\frac{1}{5}\sum\limits_{r = 1}^5 {f\left( {\frac{r}{5}} \right) < \frac{\pi }{4} < \frac{1}{5}\sum\limits_{r = 0}^4 {f\left( {\frac{r}{5}} \right)} } \)
hence \(\frac{4}{5}\sum\limits_{r = 1}^5 {f\left( {\frac{r}{5}} \right) < \pi < \frac{4}{5}\sum\limits_{r = 0}^4 {f\left( {\frac{r}{5}} \right)} } \)
so \(2.93 < \pi < 3.33\) A1A1
Note: Accept any answers that round to \(2.9\) and \(3.3\).
[5 marks]
EITHER
recognise \(\sum\limits_{r = 0}^{n - 1} {{{( - 1)}^r}{x^{2r}}} \) as a geometric series with \(r = - {x^2}\) M1
sum of \(n\) terms is \(\frac{{1 - {{( - {x^2})}^n}}}{{1 - - {x^2}}} = \frac{{1 + {{( - 1)}^{n - 1}}{x^{2n}}}}{{1 + {x^2}}}\) M1AG
OR
\(\sum\limits_{r = 0}^{n - 1} {{{( - 1)}^r}(1 + {x^2}){x^{2r}} = (1 + {x^2}){x^0} - (1 + {x^2}){x^2} + (1 + {x^2}){x^4} + \ldots } \)
\( + {( - 1)^{n - 1}}(1 + {x^2}){x^{2n - 2}}\) M1
cancelling out middle terms M1
\( = 1 + {( - 1)^{n - 1}}{x^{2n}}\) AG
[2 marks]
\(\sum\limits_{r = 0}^{n - 1} {{{( - 1)}^r}{x^{2r}} = \frac{1}{{1 + {x^2}}} + {{( - 1)}^{n - 1}}\frac{{{x^{2n}}}}{{1 + {x^2}}}} \)
integrating from \(0\) to \(1\) M1
\(\left[ {\sum\limits_{r = 0}^{n - 1} {{{( - 1)}^r}\frac{{{x^{2r + 1}}}}{{2r + 1}}} } \right]_0^1 = \int_0^1 {f(x){\text{d}}x + {{( - 1)}^{n - 1}}\int_0^1 {\frac{{{x^{2n}}}}{{1 + {x^2}}}{\text{d}}x} } \) A1A1
\(\int_0^1 {f(x){\text{d}}x = \frac{\pi }{4}} \) A1
so \(\pi = 4\left( {\sum\limits_{r = 0}^{n - 1} {\frac{{{{( - 1)}^r}}}{{2r + 1}} - {{( - 1)}^{n - 1}}\int_0^1 {\frac{{{x^{2n}}}}{{1 + {x^2}}}{\text{d}}x} } } \right)\) AG
[4 marks]
Total [14 marks]

