| Date | November 2014 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 14N.3.SL.TZ0.3 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | Time zone 0 |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | 3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
This question is about the Doppler effect.
Georgia carries out an experiment to measure the speed of mosquitoes. She sets up a microphone to record the sounds of passing mosquitoes.
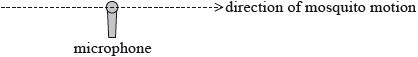
One mosquito is moving in a straight line with constant speed and passes very close to the microphone as seen in the diagram. The mosquito produces a sound of constant frequency.
The speed of sound in air is \({\text{340 m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - {\text{1}}}}\).
The maximum frequency recorded is 751 Hz and the minimum frequency recorded is 749 Hz. Explain this observation.
Determine the speed of the mosquito.
Markscheme
as the mosquito approaches the wavelength perceived by Georgia is shorter and therefore the perceived frequency is higher;
as the mosquito is moving away, the wavelength perceived is longer than the emitted and therefore the perceived frequency is lower;
due to the Doppler effect;
approaching \(751 = f \times \frac{{340}}{{340 - u}}\);
moving away \(749 = f \times \frac{{340}}{{340 + u}}\);
to produce \(u = 0.45{\text{ m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\);
or
emitted frequency is \(\frac{{751 + 749}}{2} = 750{\text{ Hz}}\);
applying the Doppler effect for approach (or recession), \(751 = 750\frac{{340}}{{340 - u}}\)\(\,\,\,\)or\(\,\,\,\)\(749 = 750\frac{{340}}{{340 + u}}\);
to produce \(u = 0.45{\text{ m}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\);
Examiners report
In (a), many candidates drew the classic diagram with wavefronts closer in front of the source and further apart behind. However, very few related this to the situation and the values given.
(b) was a more difficult question with few working through to the solution.

