| Date | November 2010 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 10N.3.SL.TZ0.F2 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 3 | Time zone | Time zone 0 |
| Command term | State | Question number | F2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
This question is about optical fibres.
State what is meant by material dispersion.
(i) The signal shown below is fed into a monomode optical fibre.
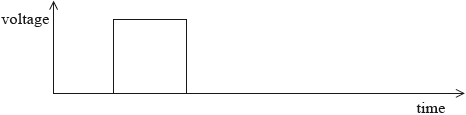
On the diagram above, show the effects of material dispersion on the input signal by drawing the shape of the signal after it has travelled a long distance in the optical fibre.
(ii) State and explain how the effects on the signal drawn in (c)(i) may be reduced.
The data in (d) are confidential and must be protected. Without taking financial costs into account, outline whether a direct optical fibre connection or a transmission through a geosynchronous satellite would be more suitable for the transfer of these data.
Markscheme
speed of propagation depends on frequency/wavelength;
(and so after some time) different frequencies cover different distances;
(i) pulse with longer duration and shorter height shown;
Ignore shape of pulse.
(ii) dispersion is caused by a range of signal frequencies/wavelengths;
so reduce range of frequencies/wavelengths / use monochromatic signal;
an optical fibre might be preferable because the data are transmitted along a protected line;
in a satellite transmission the data can be intercepted by anyone;
or
a satellite is preferable provided that it has an encryption system/encoded signal;
wider coverage than cable / any other sensible suggestion;
Examiners report
Material dispersion was often confused with modal dispersion.
In part (a) material dispersion was often confused with modal dispersion and this confusion carried through to answers to part (b) and c(ii).
The confidential transfer of data, was usually answered well.

