| Date | November 2010 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 10N.1.SL.TZ0.7 |
| Level | Standard level | Paper | Paper 1 | Time zone | Time zone 0 |
| Command term | Question number | 7 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A ball is tied to a string and rotated at a uniform speed in a vertical plane. The diagram shows the ball at its lowest position. Which arrow shows the direction of the net force acting on the ball?
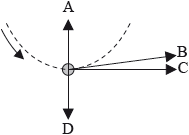
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
[N/A]
Syllabus sections
Show 57 related questions
- 17N.2.SL.TZ0.5a: Determine the orbital period for the satellite. Mass of Earth = 6.0 x 1024 kg
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.22: A satellite X of mass m orbits the Earth with a period T. What will be the orbital period of...
- 17N.1.SL.TZ0.21: A mass attached to a string rotates in a gravitational field with a constant period in a...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.8c: Outline, in terms of the force acting on it, why the Earth remains in a circular orbit around...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ2.1d: The cable is wound onto a cylinder of diameter 1.2 m. Calculate the angular velocity of the...
- 17M.2.SL.TZ1.1b.ii: The hill at point B has a circular shape with a radius of 20 m. Determine whether the skier...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.18: A small ball of weight W is attached to a string and moves in a vertical circle of radius...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.22: Two satellites of mass m and 2m orbit a planet at the same orbit radius. If F is the force...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.23: An object of constant mass is tied to the end of a rope of length l and made to move in a...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.22: A horizontal disc rotates uniformly at a constant angular velocity about a central axis...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.15: Two pulses are travelling towards each other. What is a possible pulse shape when the...
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.22: An object at the end of a wooden rod rotates in a vertical circle at a constant angular...
- 16M.1.SL.TZ0.23: ...
- 16M.1.SL.TZ0.22: A mass connected to one end of a rigid rod rotates at constant speed in a vertical plane...
- 15M.1.SL.TZ1.8: A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along...
- 15M.1.SL.TZ2.7: An electron moves with uniform circular motion in a region of magnetic field. Which diagram...
- 14M.1.SL.TZ1.8: The maximum speed with which a car can take a circular turn of radius R is v. The maximum...
- 14M.1.SL.TZ2.9: Two particles, X and Y, are attached to the surface of a horizontally mounted...
- 14M.1.HL.TZ1.9: The magnitude of the potential at the surface of a planet is V. What is the escape speed from...
- 14M.2.SL.TZ1.6d: Aibhe moves so that she is sitting at a distance of 0.75 m from the centre of the...
- 14M.2.SL.TZ1.6a: Determine the magnitude of the velocity of Aibhe relative to (i) Euan. (ii) the centre of...
- 14M.2.SL.TZ1.6b: (i) Outline why Aibhe is accelerating even though she is moving at constant speed. (ii) Draw...
- 14M.2.HL.TZ1.6h: (i) Identify the force that causes the centripetal acceleration of the spaceship. (ii)...
- 15N.2.SL.TZ0.2b: Show that the orbital speed of Phobos is about \({\text{2 km}}\,{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\).
- 15N.2.SL.TZ0.2a: Outline why Phobos moves with uniform circular motion.
- 15N.2.SL.TZ0.2c: Deduce the mass of Mars.
- 14N.1.SL.TZ0.5: An object rotates in a horizontal circle when acted on by a centripetal force F. What is the...
- 14N.1.HL.TZ0.5: An object rotates in a horizontal circle when acted on by a centripetal force F. What is the...
- 14M.2.HL.TZ2.9h: (i) Calculate the maximum speed of the car at which it can continue to move in the...
- 14M.2.SL.TZ2.6c: (i) Calculate the maximum speed of the car at which it can continue to move in the...
- 12N.1.SL.TZ0.11: What is the acceleration of an object rotating with constant speed v in a circle of radius...
- 11N.1.HL.TZ0.5: A car travels in a horizontal circle at constant speed. At any instant the resultant...
- 13N.1.SL.TZ0.8: A body moves with uniform speed around a circle of radius r. The period of the motion is T....
- 13M.2.SL.TZ1.2b: On the diagram, draw and label the vertical forces acting on the car in the position shown.
- 12M.1.SL.TZ2.8: A pendulum bob is attached to a light string and is swinging in a vertical plane. At the...
- 13M.2.SL.TZ1.2a: Explain why the car is accelerating even though it is moving with a constant speed.
- 13M.2.SL.TZ1.2c: Calculate the maximum speed at which the car will stay in contact with the bridge.
- 12M.1.HL.TZ2.5: Particle P is moving with uniform speed in a horizontal circle. Which of the following shows...
- 12M.1.SL.TZ1.8: A car moves at constant speed around a horizontal circular track. The resultant force on the...
- 13M.2.HL.TZ1.11b: A satellite of mass m orbits a planet of mass M. Derive the following relationship...
- 13M.2.HL.TZ1.11c: A polar orbiting satellite has an orbit which passes above both of the Earth’s poles. One...
- 13M.1.SL.TZ2.8: A car on a road follows a horizontal circular path at constant speed. Which of the following...
- 11N.2.SL.TZ0.4f: On its journey, the railway engine now travels around a curved track at constant speed....
- 12N.2.SL.TZ0.9b: The diagram shows a satellite orbiting the Earth. The satellite is part of the network of...
- 12N.2.SL.TZ0.9c: (i) Explain why the satellite is accelerating towards the centre of the Earth even though its...
- 11M.1.HL.TZ1.4: A particle of mass m is moving with constant speed v in uniform circular motion. What is the...
- 11M.1.SL.TZ1.9: A cyclist rides around a circular track at a uniform speed. Which of the following correctly...
- 11M.2.SL.TZ1.2a: The electron’s path while in the region of magnetic field is a quarter circle. Show that...
- 11M.2.SL.TZ1.3b: Determine the speed of rotation of the ball.
- 11M.2.HL.TZ1.2a: State why the work done by the gravitational force during one full revolution of the probe is...
- 11M.2.SL.TZ1.3a: (i) On the diagram above, draw and label arrows to represent the forces on the ball in the...
- 09M.1.SL.TZ1.8: A communications satellite is moving at a constant speed in a circular orbit around Earth. At...
- 09N.1.SL.TZ0.5: An aircraft is flying at constant speed in a horizontal circle. Which of the following...
- 10M.1.SL.TZ1.8: A particle P is moving anti-clockwise with constant speed in a horizontal circle. Which...
- 09N.1.SL.TZ0.6: For a particle moving at constant speed in a horizontal circle, the work done by the...
- 10N.2.SL.TZ0.B1Part1.a: (i) label with the letter A a point at which the acceleration of the pendulum bob is a...
- 10N.2.SL.TZ0.B1Part1.b: Explain why the magnitude of the tension in the string at the midpoint of the oscillation is...

