| Date | May 2010 | Marks available | 5 | Reference code | 10M.3.sl.TZ2.E2 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Identify and State | Question number | E2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Disposal of radioactive waste is a major ecological concern.
(a) State one source of low-level radioactive waste and one source of high-level radioactive waste.
Low-level waste:
High-level waste:
(b) Consider the following types of radioactive waste.
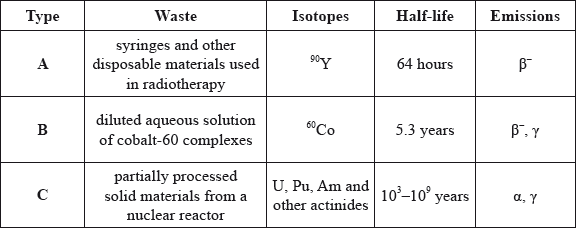
Identify which method can be used for the disposal of radioactive wastes A, B and C.
(i) Vitrification followed by long-term underground storage:
(ii) Storage in a non-shielded container for two months followed by the disposal as normal (non-radioactive) waste:
(iii) Ion-exchange and adsorption on iron(II) hydroxide, storage in a shielded container for 50 years, then mixing with concrete and shallow land burial:
Markscheme
(a) Low-level waste:
hospitals/radiotherapy/radiodiagnostics / food/seed/plant irradiators / smoke detectors / research laboratories / oil/coal/natural gas processing/burning/survey / uranium mill tailings / (supporting processes of) nuclear fuel cycle;
High-level waste:
(main processes of) nuclear fuel cycle / nuclear weapons / radioisotope thermoelectric generators;
Accept more specific processes/devices/etc. for both high and low level waste.
Do not accept radioactive elements/isotopes without references to their sources.
(b) (i) C;
(ii) A;
(iii) B;
Examiners report
This question was generally well answered, though on occasion candidates failed to be specific enough about the sources of nuclear waste. In the second part, many confused the preferred techniques of disposal for high level wastes with long and short half-lives.

