| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 18M.3.sl.TZ2.4 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Compare | Question number | 4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Propene can polymerize to form polypropene.
Propene monomer: 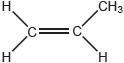
Sketch four repeating units of the polymer to show atactic and isotactic polypropene.
State the chemical reason why plastics do not degrade easily.
Compare two ways in which recycling differs from reusing plastics.
Civilizations are often characterized by the materials they use.
Suggest an advantage polymers have over materials from the iron age.
Markscheme
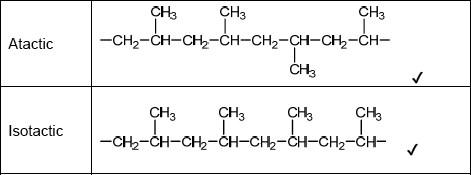
Do not accept syndiotactic (alternating orientation of the CH3 groups), eg,
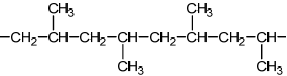
for M1 or M2.
Accept any correct atactic ordering of CH3 groups.
Penalize missing hydrogens or incorrect bond connectivities once only.
Accept skeletal structures.
Ignore continuation bonds, brackets and “n” indices in structures.
[2 marks]
strong covalent bonds
Accept “moisture cannot get inside the plastic matrix, and bacteria cannot live without moisture, so they cannot attack the polymer chains”.
Accept “bacteria lack the enzymes required to break down the hydrocarbon chains”.
[1 mark]
Any two of:
Recycling: shredded/melted/reformed AND Reuse: used in its current form
recycling is more energy intensive «than reusing»
recycling degrades the quality of plastic but reusing «typically» does not
recycling breaks down original product to form a new product whereas reuse extends product life
[2 marks]
more pliable/flexible materials
OR
more durable/non-corrosive/longer-lasting materials
OR
greater variety of materials
OR
lower density
OR
can be clear/translucent
Accept “more adaptable”.
Do not accept just “more useful”.
[1 mark]

