| Date | May 2017 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 17M.2.hl.TZ1.2 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | Describe | Question number | 2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Titanium and vanadium are consecutive elements in the first transition metal series.
\({\text{TiC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}\) reacts with water and the resulting titanium(IV) oxide can be used as a smoke screen.
Describe the bonding in metals.
Titanium exists as several isotopes. The mass spectrum of a sample of titanium gave the following data:
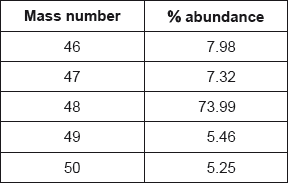
Calculate the relative atomic mass of titanium to two decimal places.
State the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the \(_{{\text{22}}}^{{\text{48}}}{\text{Ti}}\) atom.

State the full electron configuration of the \(_{{\text{22}}}^{{\text{48}}}{\text{T}}{{\text{i}}^{2 + }}\) ion.
Suggest why the melting point of vanadium is higher than that of titanium.
Sketch a graph of the first six successive ionization energies of vanadium on the axes provided.
Explain why an aluminium-titanium alloy is harder than pure aluminium.
Describe, in terms of the electrons involved, how the bond between a ligand and a central metal ion is formed.
Outline why transition metals form coloured compounds.
State the type of bonding in potassium chloride which melts at 1043 K.
A chloride of titanium, \({\text{TiC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}\), melts at 248 K. Suggest why the melting point is so much lower than that of KCl.
Formulate an equation for this reaction.
Suggest one disadvantage of using this smoke in an enclosed space.
Markscheme
electrostatic attraction
between «a lattice of» metal/positive ions/cations AND «a sea of» delocalized electrons
Accept “mobile electrons”.
Do not accept “metal atoms/nuclei”.
[2 marks]
\(\frac{{(46 \times 7.98){\text{ + }}(47 \times 7.32){\text{ + }}(48 \times 73.99){\text{ + }}(49 \times 5.46){\text{ + }}(50 \times 5.25)}}{{100}} = 47.93\)
Answer must have two decimal places with a value from 47.90 to 48.00.
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Award [0] for 47.87 (data booklet value).
[2 marks]
Protons: 22 AND Neutrons: 26 AND Electrons: 22
[1 mark]
\({\text{1}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}{\text{3}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{3}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}{\text{3}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{2}}}\)
[1 mark]
vanadium has smaller ionic radius «leading to stronger metallic bonding»
Accept vanadium has «one» more valence electron«s» «leading to stronger metallic bonding».
Accept “atomic” for “ionic”.
[1 mark]
regular increase for first five AND sharp increase to the 6th
A log graph is acceptable.
Accept log plot on given axes (without amendment of y-axis).
Award mark if gradient of 5 to 6 is greater than “best fit line” of 1 to 5.
[1 mark]
titanium atoms/ions distort the regular arrangement of atoms/ions
OR
titanium atoms/ions are a different size to aluminium «atoms/ions»
prevent layers sliding over each other
Accept diagram showing different sizes of atoms/ions.
[2 marks]
pair of electrons provided by the ligand
Do not accept “dative” or “coordinate bonding” alone.
[1 mark]
partially filled d-orbitals
«ligands cause» d-orbitals «to» split
light is absorbed as electrons transit to a higher energy level «in d–d transitions»
OR
light is absorbed as electrons are promoted
energy gap corresponds to light in the visible region of the spectrum
colour observed is the complementary colour
[4 marks]
ionic
OR
«electrostatic» attraction between oppositely charged ions
[1 mark]
«simple» molecular structure
OR
weak«er» intermolecular bonds
OR
weak«er» bonds between molecules
Accept specific examples of weak bonds such as London/dispersion and van der Waals.
Do not accept “covalent”.
[1 mark]
\({\text{TiC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{(l)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}} \to {\text{Ti}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(s)}} + {\text{4HCl(aq)}}\) correct products
correct balancing
Accept ionic equation.
Award M2 if products are HCl and a compound of Ti and O.
[2 marks]
HCl causes breathing/respiratory problems
OR
HCl is an irritant
OR
HCl is toxic
OR
HCl has acidic vapour
OR
HCl is corrosive
Accept TiO2 causes breathing
problems/is an irritant.
Accept “harmful” for both HCl and TiO2.
Accept “smoke is asphyxiant”.
[1 mark]

