| Date | May 2011 | Marks available | 10 | Reference code | 11M.2.bp.4 |
| Level | SL and HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | |
| Command term | Examine | Question number | 4 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
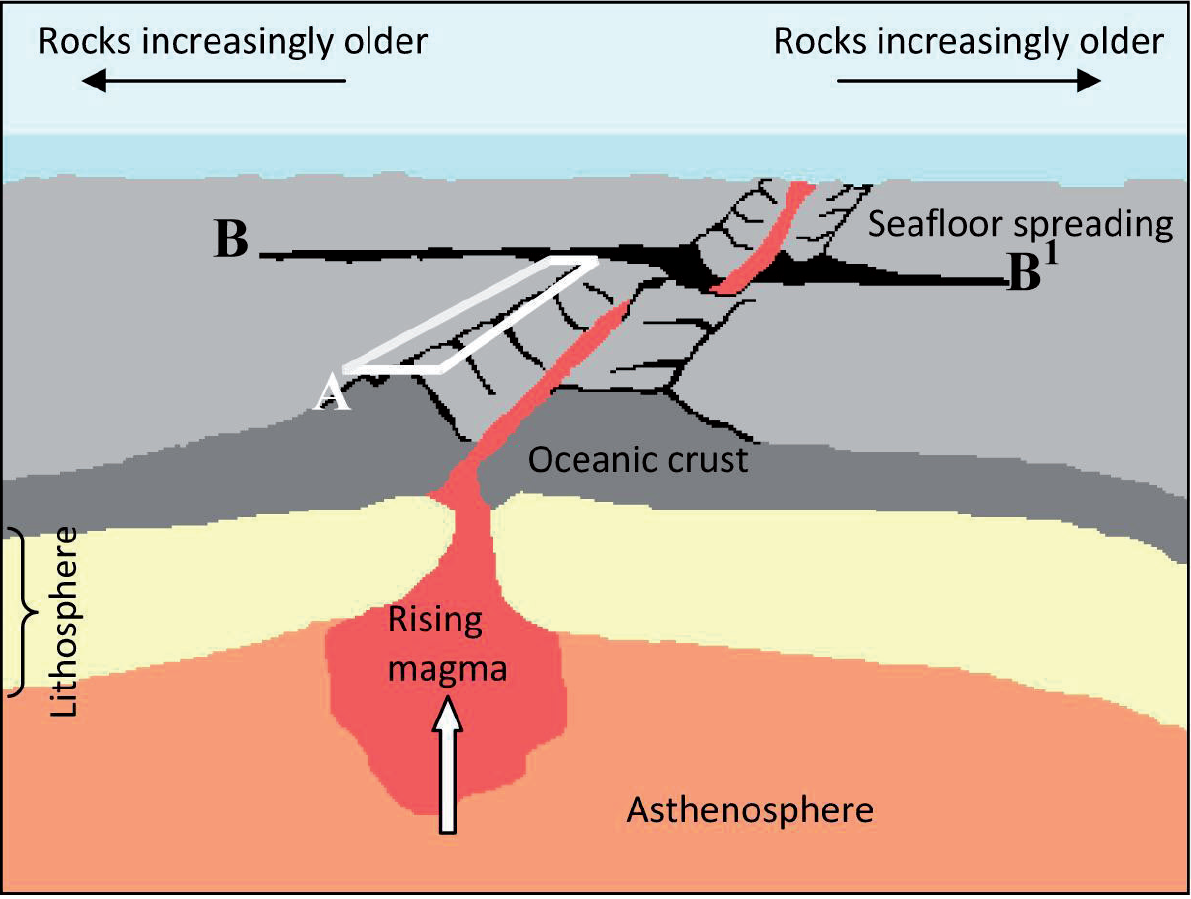
The diagram shows some of the main features of the ocean floor.
©International Baccalaureate 2013
Referring to the diagram, identify feature A and feature B–B1.
Explain why the ocean floor becomes increasingly older with distance from A.
Using an annotated diagram only, explain the formation of an ocean trench.
Examine why oceans are areas of geopolitical conflict.
Markscheme
A: Rift valley or ridge system or ocean ridge. Diverging or constructive plate boundary is also acceptable.
B–B1: Transform or transcurrent faults. Slipping fault/tear fault or a fault may also be acceptable.
As a result of sea floor spreading and the creation of newly “constructed” ocean floor at the constructive boundary [1 mark], the age of the floor increases with distance and the oldest floor is found, therefore, furthest away from the ridge and rift systems [1 mark].
The features of the trench should be clearly illustrated and explained on a diagram. The diagram should include:
- a trench where two plates are converging [1 mark]
- direction of plate movement [1 mark]
- the concept of subduction [1 mark].
Further 3 marks for explanatory annotations that identify:
- plate density
- convection cell
- sedimentation
- earthquakes along the Benioff zone
- or labeling that shows relevant located examples.
Award a maximum of 4 marks for a labeled diagram with an explanation which is separate from the diagram.
Award a maximum of 2 marks for an explanation without a diagram.
Likely sources of geopolitical conflict include: disputed islands, extended fishing zones, oil exploration, the possibility of gas extraction in the Arctic or hydrogen reserves in the Atlantic, use of Arctic and Antarctic areas.
As technology advances and exploration techniques improve, the potential of oceans as a source of biotic and abiotic resources has been realized. The need for these resources has resulted in nations extending, or wanting to extend, their boundaries, laying claim to substantial portions of continental shelves or areas which are now accessible due to ice melt. This may lead to altercations between nations who lay claim to the same areas of ocean floor or islands.
The emphasis must be placed on conflict and this may be the potential for armed conflict or political dialogue/negotiation.
Answers which examine a conflict in detail are likely to be credited at bands E and F.
Marks should be allocated according to the markbands.
Examiners report
The mid ocean ridge/rift valley system (A) was almost universally identified whereas the transform fault (B–B1) was almost universally not identified, in fact very few candidates recognized it as a fault, which would have been credited.
Most candidates provided a good explanation of why the ocean floor gets older with distance from the central ridge.
In general, candidates provided good diagrams of the formation of ocean trenches although many candidates provided descriptive labels rather than explanatory annotations.
Generally, this was answered well, with support mainly coming from the Arctic and its geopolitical conflict, though at standard level there was little reference to other important ocean areas of conflict, giving the responses too narrow a focus to reach the higher mark range.

