| Date | November 2021 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 21N.1.HL.TZ0.5 |
| Level | Higher level | Paper | Paper 1 | Time zone | 0 - no time zone |
| Command term | Question number | 5 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A cyclist rides up a hill of vertical height 100 m in 500 s at a constant speed. The combined mass of the cyclist and the bicycle is 80 kg. The power developed by the cyclist is 200 W. What is the efficiency of the energy transfer in this system?
A. 8 %
B. 20 %
C. 60 %
D. 80 %
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.7: A student of weight 600N climbs a vertical ladder 6.0m tall in a time of 8.0s. What is the...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.7c.ii:
Show that the kinetic energy of the object is about 0.7 mJ.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.8: A car travelling at a constant velocity covers a distance of 100 m in 5.0 s. The thrust of...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.6: The initial kinetic energy of a block moving on a horizontal floor is 48 J. A constant...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.1e:
A second identical ball is placed at the bottom of the bowl and the first ball is displaced so that its height from the horizontal is equal to 8.0 m.
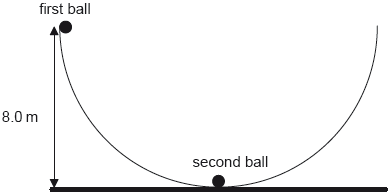
The first ball is released and eventually strikes the second ball. The two balls remain in contact. Determine, in m, the maximum height reached by the two balls.
- 18M.1.SL.TZ2.3: A motor of input power 160 W raises a mass of 8.0 kg vertically at a constant speed of 0.50 m...
-
17N.1.SL.TZ0.7:
A system that consists of a single spring stores a total elastic potential energy Ep when a load is added to the spring. Another identical spring connected in parallel is added to the system. The same load is now applied to the parallel springs.
What is the total elastic potential energy stored in the changed system?
A. Ep
B.
C.
D.
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.15: Two pulses are travelling towards each other. What is a possible pulse shape when the...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ1.7: A graph shows the variation of force acting on an object moving in a straight line with...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.5:
A horizontal spring of spring constant k and negligible mass is compressed through a distance y from its equilibrium length. An object of mass m that moves on a frictionless surface is placed at the end of the spring. The spring is released and returns to its equilibrium length.
What is the speed of the object just after it leaves the spring?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18N.1.SL.TZ0.8:
A compressed spring is used to launch an object along a horizontal frictionless surface. When the spring is compressed through a distance and released, the object leaves the spring at speed . What is the distance through which the spring must be compressed for the object to leave the spring at ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 18N.1.SL.TZ0.7: The mass at the end of a pendulum is made to move in a horizontal circle of radius r...
- 18N.2.SL.TZ0.3b: Explain why the egg is likely to break when dropped onto concrete from the same height.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.i:
Show that the kinetic energy of the egg just before impact is about 0.6 J.
-
19N.2.SL.TZ0.4b(i):
Show that the radius of the path is about 6 cm.
- 19N.1.SL.TZ0.7: A ball is thrown vertically upwards. Air resistance is negligible. What is the variation with...
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.iii: Explain why the egg is likely to break when dropped onto concrete from the same height.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.6: A nuclear particle has an energy of 108 eV. A grain of sand has a mass of 32 mg. What speed...
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.6: A block rests on a frictionless horizontal surface. An air rifle pellet is fired horizontally...
-
19M.1.SL.TZ1.6:
An object of mass m is sliding down a ramp at constant speed. During the motion it travels a distance along the ramp and falls through a vertical distance h. The coefficient of dynamic friction between the ramp and the object is μ. What is the total energy transferred into thermal energy when the object travels distance ?
A. mgh
B. mgx
C. μmgh
D. μmgx
-
19M.2.SL.TZ1.1a.iii:
Friction and air resistance act on the bicycle and the girl when they move. Assume that all the energy is transferred from the battery to the electric motor. Determine the total average resistive force that acts on the bicycle and the girl.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.6b.iii:
Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation of gravitational potential energy with time for the bob and the object after the collision. The data from the graph used in (a) is shown as a dashed line for reference.
- 19M.1.SL.TZ2.7: An astronaut is moving at a constant velocity in the absence of a gravitational field when he...
-
19M.2.SL.TZ2.1aii:
Calculate the average power delivered to the ball during the impact.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.1biii:
Determine the speed of the tennis ball as it strikes the ground.
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.7: An object of mass 2kg is thrown vertically downwards with an initial kinetic energy of 100J....
-
21N.1.SL.TZ0.8:
A net force acts on an object of mass that is initially at rest. The object moves in a straight line. The variation of with the distance is shown.
What is the speed of the object at the distance ?
A.B.
C.
D.
- 16N.1.SL.TZ0.5: An object, initially at rest, is accelerated by a constant force. Which graphs show the...
-
21M.2.SL.TZ1.3a.i:
The molar mass of water is 18 g mol−1. Estimate the average speed of the water molecules in the vapor produced. Assume the vapor behaves as an ideal gas.
- 19M.1.SL.TZ2.6: A boat with an output engine power of 15 kW moves through water at a speed of 10 m s-1. What...
- 21N.1.SL.TZ0.20: An electric motor of efficiency 0.75 is connected to a power supply with an emf of 20 V and...
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.5:
A mass m attached to a string of length R moves in a vertical circle with a constant speed. The tension in the string at the top of the circle is T. What is the kinetic energy of the mass at the top of the circle?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.2.SL.TZ1.1d:
The length reached by the rope at C is 77.4 m. Suggest how energy considerations could be used to determine the elastic constant of the rope.
-
19N.2.SL.TZ0.1c:
Determine, with reference to the work done by the average force, the horizontal distance travelled by the ball while it was in contact with the racket.
-
18M.2.SL.TZ2.1d:
A second identical ball is placed at the bottom of the bowl and the first ball is displaced so that its height from the horizontal is equal to 8.0 m.

The first ball is released and eventually strikes the second ball. The two balls remain in contact. Determine, in m, the maximum height reached by the two balls.
- 22M.1.SL.TZ2.9: Two blocks of different masses are released from identical springs of elastic constant k =...
-
20N.1.SL.TZ0.19:
An electric motor raises an object of weight through a vertical distance of in . The current in the electric motor is at a potential difference of . What is the efficiency of the electric motor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.1.SL.TZ0.3:
An object of mass moving at velocity collides with a stationary object of mass . The objects stick together after the collision. What is the final speed and the change in total kinetic energy immediately after the collision?
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.5: A car is driven from rest along a straight horizontal road. The car engine exerts a constant...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1d:
The length reached by the rope at C is 77.4 m. Suggest how energy considerations could be used to determine the elastic constant of the rope.
-
17M.2.SL.TZ1.1a.i:
From A to B, 24 % of the gravitational potential energy transferred to kinetic energy. Show that the velocity at B is 12 m s–1.
-
19N.1.SL.TZ0.8:
The tension in a horizontal spring is directly proportional to the extension of the spring. The energy stored in the spring at extension is . What is the work done by the spring when its extension changes from to ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
17M.2.SL.TZ2.1c:
The cable is pulled by an electric motor. The motor has an overall efficiency of 23 %. Determine the average power input to the motor.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.ii:
An electron is emitted from the photoelectric surface with kinetic energy 2.1 eV. Calculate the speed of the electron at the collecting plate.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.7: A force acts on an object of mass 40 kg. The graph shows how the acceleration a of the object...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.5:
A mass is released from the top of a smooth ramp of height . After leaving the ramp, the mass slides on a rough horizontal surface.
The mass comes to rest in a distance d. What is the coefficient of dynamic friction between the mass and the horizontal surface?
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.6: Masses X and Y rest on a smooth horizontal surface and are connected by a massless spring....
- 21M.1.SL.TZ1.5: A car takes 20 minutes to climb a hill at constant speed. The mass of the car is 1200 kg and...
- 21M.1.SL.TZ1.9: An electron has a linear momentum of 4.0 × 10−25 kg m s−1. What is the order of magnitude...
- 21M.1.SL.TZ2.8: A projectile is launched upwards at an angle θ to the horizontal with an initial momentum p0...
-
21M.1.SL.TZ2.9:
The graph shows the variation with distance of a horizontal force acting on an object. The object, initially at rest, moves horizontally through a distance of .
A constant frictional force of opposes the motion. What is the final kinetic energy of the object after it has moved ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.1.SL.TZ1.5:
An object falls from rest from a height h close to the surface of the Moon. The Moon has no atmosphere.
When the object has fallen to height above the surface, what is
?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
19M.2.SL.TZ2.1biii:
Determine the speed of the tennis ball as it strikes the ground.
-
19N.1.SL.TZ0.22:
An object of mass m makes n revolutions per second around a circle of radius r at a constant speed. What is the kinetic energy of the object?
A. 0
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.1a(iv):
Calculate the power transferred to the air by the aircraft.
-
20N.1.SL.TZ0.4:
An object of mass is thrown downwards from a height of . The initial speed of the object is .
The object hits the ground at a speed of . Assume . What is the best estimate of the energy transferred from the object to the air as it falls?A.
B.
C.
D.
- 19M.2.SL.TZ1.1c: On another journey up the slope, the girl carries an additional mass. Explain whether...
-
19M.1.SL.TZ2.5:
An object has a weight of 6.10 × 102 N. What is the change in gravitational potential energy of the object when it moves through 8.0 m vertically?
A. 5 kJ
B. 4.9 kJ
C. 4.88 kJ
D. 4.880 kJ
- 19M.2.SL.TZ1.5c: Describe the changes in gravitational potential energy of the oscillating system from t = 0...
- 17M.1.SL.TZ2.7: The efficiency of an electric motor is 20 %. When lifting a body 500 J of energy are...
- 18M.1.SL.TZ1.7: An increasing force acts on a metal wire and the wire extends from an initial length l0 to a...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.1aii:
Calculate the average power delivered to the ball during the impact.
-
19M.2.SL.TZ1.6c.ii:
Outline why this force does no work on the Moon.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.5a.ii:
Outline why this force does no work on Phobos.
-
21M.2.SL.TZ1.1d.i:
Determine the kinetic energy of the ball immediately after the bounce.
- 21N.1.SL.TZ0.7: An object of mass 1.0 kg hangs at rest from a spring. The spring has a negligible mass and...
-
21N.2.SL.TZ0.1d.i:
Determine the average force exerted on the floor by the ball.
-
21N.2.SL.TZ0.1c:
Estimate the loss in the mechanical energy of the ball as a result of the collision with the floor.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.4b.ii:
The plutonium nucleus is at rest when it decays.
Calculate the ratio .
-
21N.2.SL.TZ0.5b.ii:
The plutonium nucleus is at rest when it decays.
Calculate the ratio .
-
22M.1.SL.TZ1.8:
A cart travels from rest along a horizontal surface with a constant acceleration. What is the variation of the kinetic energy Ek of the cart with its distance s travelled? Air resistance is negligible.

