| Date | November 2013 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 13N.1.bp.3 |
| Level | SL and HL | Paper | 1 | Time zone | |
| Command term | Identify | Question number | 3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The graph shows the categories of global water consumption in 2010.
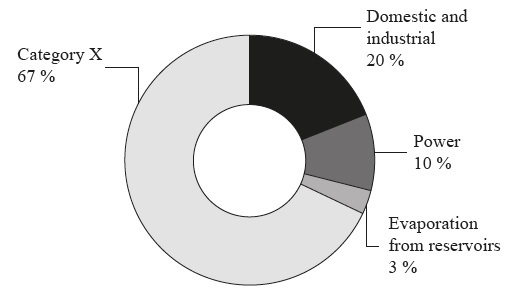
[Source: World Bank Development Report 2010. http://wdronline.worldbank.org/worldbank/a/c.html/world_development_report_2010/chapter_3_managing_land_water_feed_billion_people_protect_natural_systems/page/1 Used with permission]
Identify Category X on the diagram.
Define the term physical water scarcity.
Explain two physical factors that affect the availability of safe drinking water for a community.
Analyse the role of water in the causes of soil degradation.
Markscheme
Agriculture/farming [1 mark].
Physical water scarcity occurs when the use of water resources [1 mark] approaches or exceeds sustainable levels [1 mark] (that is, it relates water availability to demand, meaning that arid areas are not necessarily water-scarce areas if demand is small).
For a partial definition, eg water demand exceeds supply, award [1 mark] only.
Award [1 mark] for each factor and a further [1 mark] for explaining why it relates to a safe water supply.
Physical factors that affect access to safe water include climate (amount, type and timing of precipitation eg drought; climate change), geology (groundwater and aquifers), relief (surface water depressions, poor access probable if slopes are steep), drainage (rivers, lakes), isolation or distance from supply, natural hazard events such as earthquakes.
Note that the factor must be physical. This may lead to contamination, eg earthquakes lead to contamination by sewage. Do not award human factors alone such as industrial or agricultural pollution.
At least two ideas associated with causes should be developed for the award of the full [4 marks]. A greater range of ideas (in less depth) may also be awarded full marks.
Possibilities include: erosion by water, removing soil, may follow overgrazing and the removal of vegetation. Flash floods can strip surface soil within minutes, leaving barren rock. The upward movement of water through soil may result in salinization, rendering the soils infertile. The downward movement of water through soils may leach valuable minerals out of the soil, reducing its fertility.

